Acute Gout Attack
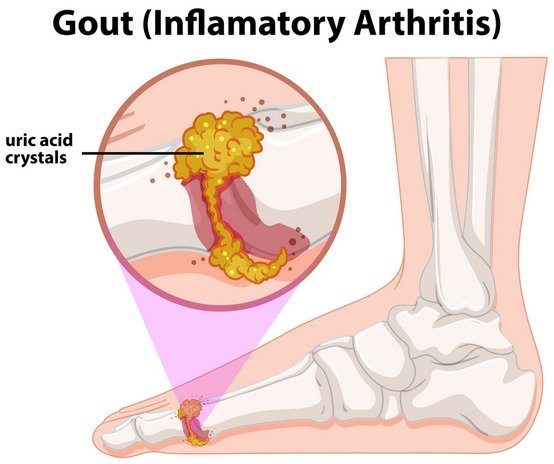
Gout is a form of arthritis, hence also called gouty arthritis. It causes moderate to severe pain and discomfort in the joints. A typical acute gouty attack is defined as the sudden onset of severe pain, redness, warmth, and swelling of a joint.
The joint most commonly affected in acute gout is the big toe (the first metatarsophalangeal joint) and is called podagra. Less likely, other joint may be involved in a gout attack with the most frequent sites being in the ankles, feet, knees, fingers, wrists, and elbows.
After onset, an acute gouty attack will usually reach its peak in 12 to 24 hours and then slowly begin to settle even without treatment. Complete recovery from the attack takes approximately 7 to 14 days without treatment and 3 to 4 days with treatment.
Dr. Thomas Sydenham elegantly wrote an accurate description of the acute gouty attack in 1683, who himself had gout:
The sufferer goes to bed and sleeps in good health. He is awakened by severe pain in the great toe about 2 a.m.; more rarely in the ankle, heel or instep. The pain is like that of joint dislocation, and yet the affected part feel as if cold water were poured over it. It is followed by mild fever, chills, and shiver. The pain which was moderate at first will become more intense. The chills and shivers increase also increase with its intensity. After a while, these symptoms come to full height, accommodating themselves to the ligaments and bones of the tarsus and metatarsus. Now it is a gnawing pain – now it is a violent tearing of the ligaments and now a tightening and pressure feeling.