Anaphylactic Complications
Anaphylactic shock is not a common outcome of what starts as anaphylaxis. Early intervention of anaphylaxis can prevent progression to the state of shock. Respiratory and cardiovascular depression is the hallmark of anaphylactic shock. Shock can be fatal, due to irreversible damage. It ensues as a cycle, where the already existing defects are amplified due to the combined failure of organs at multiple levels. [3]
Respiratory complications
- Laryngeal edema: Larynx forms a muscular airway passage to the lungs, and is located in the throat region. Anaphylaxis can lead to swelling of this passage, obstructing the flow of air, any swallowed food, and/or speech. Coupled with enlarged tongue, unattended patients can have a fatal outcome.
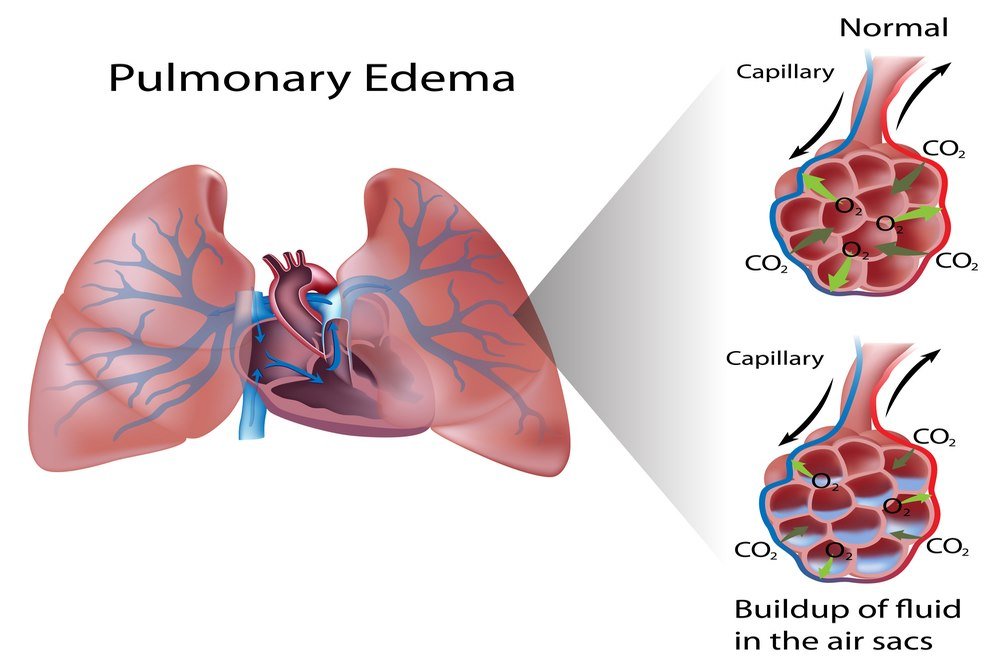
- Pulmonary edema: A common outcome of anaphylactic shock is accumulation of fluid within the lungs. The fluid around the lungs severely compromises breathing tendency, chest flexibility to allow breathing, and also impairs air exchange between the lungs and blood, which further impairs the ability of blood to perfuse essential organs. This causes acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respiratory collapse is the primary reason of death due to anaphylactic shock.
