Radiations
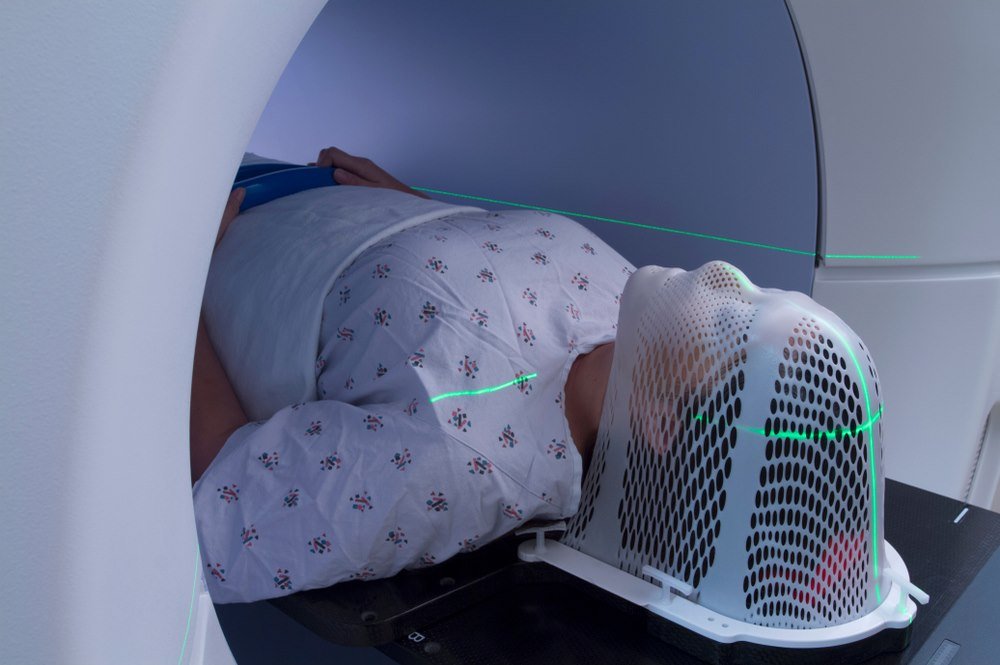
In order to treat the tumor, radiation therapy is also employed. The radiation consists of high energy X-rays or other particles that are used to destroy tumor cells. Sometimes, cancerous cells or tumor is incompletely excised. These cells can easily be removed with the help of radiations. Tumor located in a critical zone inapproachable by surgery, is also treated through radiation therapy.
The high dose of radiations destroys or deteriorates the DNA present in the tumor cells. When the damage in DNA becomes permanent, the cells die and get replaced. But the radiation not only kills the cancerous cells, it also kills the healthy brain cells. These radiations are given under strict consideration so that it causes most damage to the tumor cells and the least damage to the healthy cells.
- Internal radiation therapy:
During this process, the neurologist inserts a radioactive material near the site or inside the tumor. It does not cause the body to become radioactive. It is also called brachytherapy. It is used with a combination of other cancer treatments. The radioactive seeds emit a high dose of radiation into a small area.
- External beam therapy:
External beam therapy consists of radiations that are used from outside, directed towards the tumor in order to destroy tumor cells. Different types of radiation therapy include photon therapy, conventional radiation therapy and 3D-CRT.
The side effects of radiation treatment include:
- Hair loss
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Memory impairments
- Loss of vision, etc.
