Trouble Swallowing
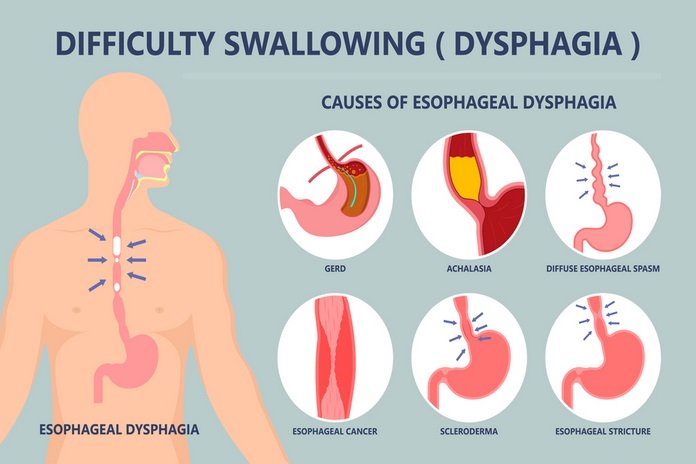
The symptom of esophageal cancer which is most common is a problem swallowing (also known as dysphagia). In this problem, it may feel like the particles of food are stuck in the throat or the chest, and may even cause the person to choke on their own food. This is often moderate when it starts and then gets unpleasant over time as the growth of cancer occurs and the opening inside the esophageal portion gets smaller.
When swallowing becomes difficult, people often make alterations in their habits of diet and eating without perceiving it. They take bites of smaller size than previous ones and chew their food in a more careful and slow manner. As cancer enlarges, the issue can get worse. The individuals then might start a diet comprising softer foods that can pass via the esophagus more easily. They might not eat bread and meat, as these foods get stuck often. The issue of swallowing may even get unpleasant to an extent that some individuals stop eating solid meals completely and switch to a diet containing liquids only. If cancer keeps dividing, even liquids might be hard to swallow at some point.
To help in passing the food through the esophagus, the glands of the body make more saliva. However, this may cause some individuals to complain of the formation of lots of saliva (spit) or mucus which is thick in nature.
