Degenerative spine disorders
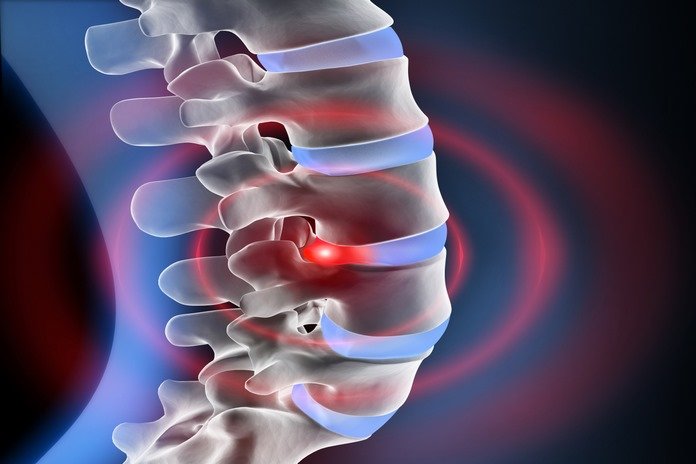
Degenerative spine disorders refer to a progressive spinal disease that worsens over time, usually triggered by old age but sometimes caused by other environmental factors.
Degenerative disc disease
Causes
Degenerative disc disease is a problem in the spinal discs, which separate one vertebra from the other. It is a progressive change of this spinal disc that may be triggered by:
Water loss: The spinal discs are dried out as we get older. This water loss is associated with padding loss between the vertebrae.
Injuries and tears: We undergo various injuries and microscopic tears every day. When the wall of the discs break, the inner core pushes through and bulges out of place.
Excessive pressure: This problem is more likely in people with structural problems in the spine such as scoliosis. There’s an uneven pressure in the spine (an excess in one side and not enough in the other) which leads to progressive and asymmetric wear down of the discs.
Risk factors
Patients with the following risk factors have a higher chance of suffering from degenerative disc disease:
A family history of musculoskeletal disease or chronic back pain
Strenuous sports activities
Prolonged sitting or a very poor posture
Obesity
Weak core muscles
Smoking
Symptoms
Pain located in the lower back, upper thigs or buttocks
Tingling and numbness in your legs and arms
Muscle weakness
Pain symptoms are not continuous. They rather come and go at times
The symptoms worsen when the patient sits down or makes a bending or twisting movement
The symptoms improve when the patient is walking, moving, or changing positions
Diagnosis
To diagnose this disease, your doctor must first collect a medical history from you, starting with your symptoms. It is important to let him know when did you start noticing the symptoms, what part of the back hurts and when.
In the physical exam, you might be asked to bend, walk, sit, and change positions to evaluate pain and how it changes. Imaging exams are also important, especially an X-Ray scan, and an MRI if your doctor suspects nerve damage.
Treatment
Medical treatment of degenerative disc disease required pain relievers such as ibuprofen and aspirin to reduce swelling and control pain. In some cases, this disease also leads to muscle spasms, and there are medications for that, too.
Physical therapy is also important in these patients to recover or prevent losing flexibility. On the long-term, physical therapy and medication lead to pain relief and recovery of the function. In some cases, pain can only be managed with steroid shots to numb the nerves or surgery to remove the injured area of the disc.
Home remedies
If you’re suffering from this problem, these recommendations can be very helpful for you:
If you don’t have a flare-up, go out frequently and move around. Physical activity is very important.
Maintain a good posture and avoid slouching
During flare-ups, you can use cold compresses to reduce pain and swelling. Hot compresses are also useful to relax tense muscles.
