Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
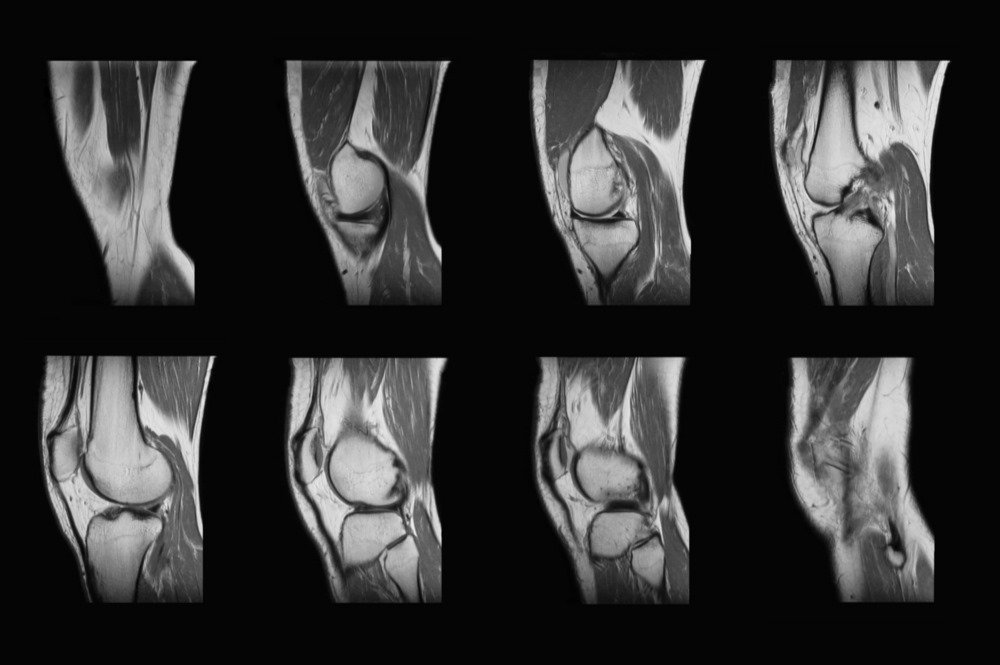
The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) accompanies the use of radio waves with a powerful magnet to attain 3D scans of the internal structures in your knee. The MRI technology gives the scans which are particularly helpful in detecting injuries to soft tissues like tendons, muscles, cartilage and ligaments. [4] The radiographic scans of the patient provide the doctor a clear image of any tissue tenderness and other knee joint conditions, thus making it easy to diagnose the actual cause of the knee problem.
The 3D scan is actually sufficient to give the patellofemoral joint view, lateral view, and the anteroposterior view of the knee joint to accurately diagnose the cause of knee problems. The radio waves give the image of the femoral condyles and this view is very helpful in detecting the presence of ostoechondritis dissecans. In the case of teenage patients with knee problems, the MRI scans indicate knee joint effusions by giving a tunnel or notch view of the knee.
