HPV Types
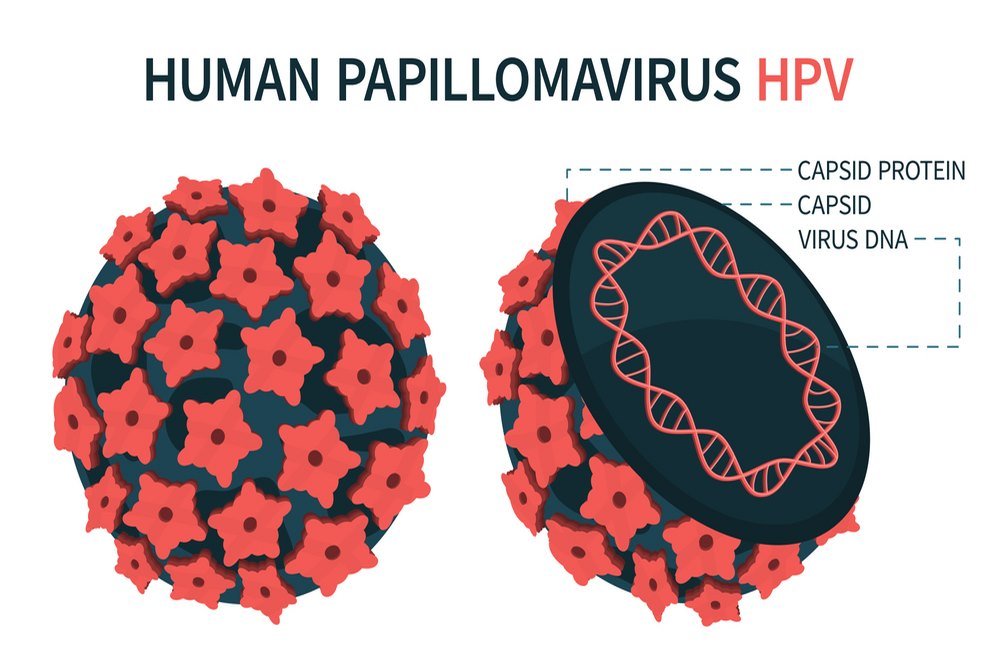
Human papilloma virus presents with two major types of symptoms, that is, when it is symptomatic. These can be categorized as benign warts, and malignant lesions in various soft tissues of the body. Certain strains of HPV have a strong disposition to cause only one type of symptom, on the basis of which they are grouped as under:
Low-risk HPV
As the name indicates, this group contains virus strains that cause either no symptoms or mild symptoms. There is a little risk of complications and no significant morbidity and mortality in relation to these strains. These trains account for about 15% of total HPV strains identified. Even among these, the most common strains are HPV 6 and 11. These are responsible for causing about 90% of the HPV warts. The warts are benign lesion caused by increased cellular division in the cells. But this proliferation is self –limiting. HPV 11, however, has a 1-3% chance of causing abnormal behavior in cellular division. The warts can appear anywhere, from the palms and soles to the face, in and around the genital structures, vagina or cervix in females, and anal region may be involved in both sexes. These warts are not harmful, and tend to go away on their own. Although available, no thorough medical treatment is required for simple warts. Most people even fail to notice the genital warts.
However, these strains are stubborn, even after the treatments that some people opt for, there is no telling if the virus has been eradicated from the body. There is a high recurrence rate, anytime later in life.
Another versatility of these types, is that it can affect people of any age, from children to young adults and sexually active population, without having a very significant preference of sex.
The warts can be cutaneous in origin or mucosal. The cutaneous warts affect the superficial layer of skin. Mucosal warts involve the inner, shining, soft and mostly reddish layer lining the insides of organs. The warts that appear in the oral cavity, gums, tongue, or the throat, are mucosal in origin.
