Treatment and Medication (Drug list)
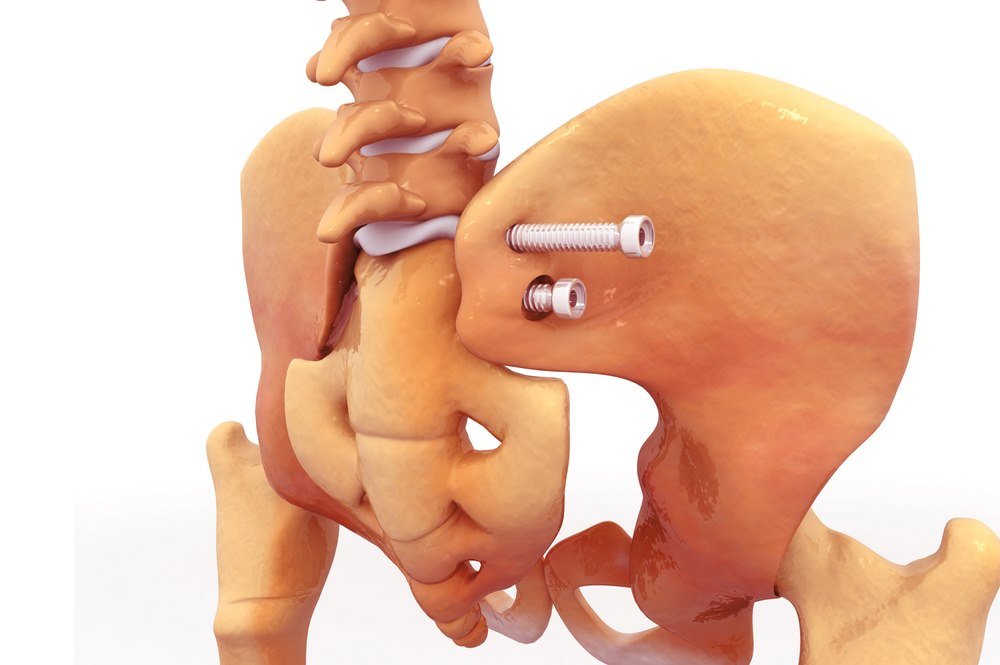
Osteoporosis progresses silently, to the point where it manifests itself by a non-traumatic fracture in the wrist, pelvic bone or the spinal vertebra. In case, osteoporosis comes to light due to such a fracture, the immediate treatment would include dealing with the fracture.
Treatment of the fracture:
- Fracture reduction: the broken bone is held back in place and allowed to grow back in place. This can be a painful process.
- Immobilization: the affected limb is immobilized by a cast to ensure alignment in place.
- Pain reduction: analgesics can be given to reduce the pain of the fractured bone.
- Rehabilitative exercise: muscles are mobilized by exercises to recover functional ability. Light and planned exercise help in restoring the ability of the bone to bear weight.
It may take generally around 6-12 weeks to heal a fracture but it depends upon the age and sex of the patient, general physical health, and bone health of the patient
Co-morbidities
Once the fracture is healed, medicines are used as a preventive measure. None of the following medicines are curative and may have associated side-effects.
Bisphosphonates

Bisphosphonates are the first line of treatment in the treatment of osteoporosis. They inhibit the osteoclastic activity and prevent bone resorption. This line of treatment is equally effective in both men and women. It can be taken orally, and is also available as an injection. It has to be taken on an empty stomach, and avoidance of food and drinks is advised for 30 minutes to an hour afterwards.
Drugs available in this class include:
- Alendronate
- Risedronate
This line of treatment requires 6-12 months to produce desired results, and in some case the treatment will be required to carry on for years.
Bisphosphonates can cause osteonecrosis of the jaw bone as a rare side-effect. A thorough dental check-up is advised before starting therapy with bisphosphonates.
SERMs
Selective Estrogen Receptors Modulators are drugs that can help prevent bone loss by having the estrogen like positive effect on the bone. They promote bone density. Raloxifene is the clinically proven drug in this class. SERMs can also have side effects, which are also due to activation of estrogen receptors in different organs:
- Hot flushes
- Blood clotting
- Leg cramps
- Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormones generally promote bone resorption, but when it is administered in small doses intermittently, it can boost the osteoblasts activity by causing their proliferation and decreasing their apoptotic death. This positive effect on bone density and mass is employed in parathyroid hormone related drugs used in osteoporosis treatment. Parathyroid hormone related drugs or other bone-building drugs are as under:
Teriparatide: is administered as a daily subdermal injection, for two years. It promotes the synthesis of new bone matrix
Romosozumab: relatively new drug, administered once monthly.
All these drugs have to be given in combined therapy with other anti-osteoporosis drugs to maintain bone health. PTH therapy is not the first line of treatment, and is only used in patients, refractory to other types of treatments. Nausea is a common side effect.
