Carotid endarterectomy surgery (CEA)
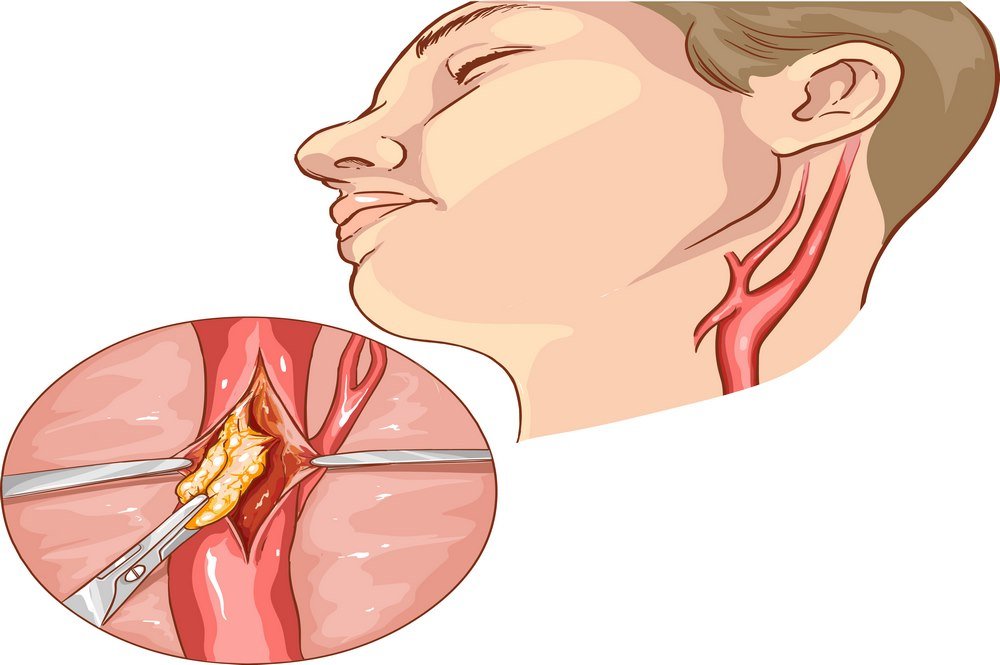
this method is used in the case of a clot in the carotid artery that lies in the neck and carries blood to the brain. After general or local anesthesia, the neurosurgeon makes a small incision through the carotid artery to retrieve the clot. In doing so the artery lumen is also widened, which also helps in re-establishing blood flow. This surgical method can have certain complications. It has the advantage of a short recovery time, although, it is advised to avoid physical exertion following a month after surgery.
There are potential risks to the CAS and CEA procedures. A dislocated clot is liable to travel within the bloodstream and may plug any other small vessel. Secondly, restoring the blood supply to the ischemic tissue can result in hyperperfusion, increased risk of oxidative damage to the tissue, or bleeding, posing an increased risk of hemorrhage.
