Types Of Thrombocytopenia
There are many genetic and environmental factors associated with the development of thrombocytopenia. Depending upon the causes, it has been divided into few categories. Some of the specific types of thrombocytopenia include;
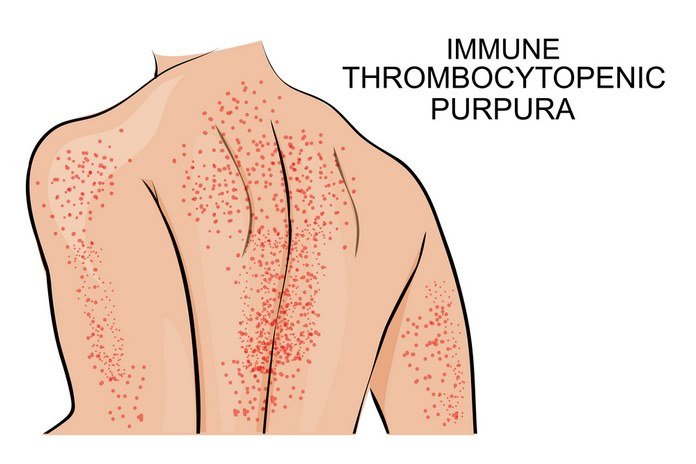
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
It is a type of thrombocytopenia caused by increased platelet destruction or decreased platelet production in the bone marrow. ITP is a medical term that describes low blood count. Idiopathic or immune thrombocytopenic purpura can cause bruising, bleeding, and immune reactions. Antibodies can cause the problem of ITP. These antibodies are produced in the body to defend against foreign materials, including bacteria and viruses. These antibodies usually prevent infection, but they can also act abnormally and can affect healthy tissues also. The condition occurs when the immune cells that produce antibodies receive mixed signals and consider a normal tissue as foreign tissue and reject it. In ITP, the platelets are recognized as invaders or foreigners to the immune system, and antibodies are created against them. The antibodies then destroy the platelet and inhibit its production.
ITP is not limited to any age group and can affect both children and adults. However, it seems to be more common in women at younger ages, while in adults, it’s common in males.
ITP can be acute and chronic. Chronic ITP can last from weeks to months. The common symptoms seen in ITP include bleeding from cuts, urine, stool, and nose. Females suffer from heavy menstruation, and bruises can also be seen on the body of ITP patients.
The people of ITP are asked to limit the intake of alcohol as it reduces the number of platelets in the body and can have an adverse effect on platelets’ efficiency in blood clotting. Also, the use of drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen should be avoided as they can affect platelet function.