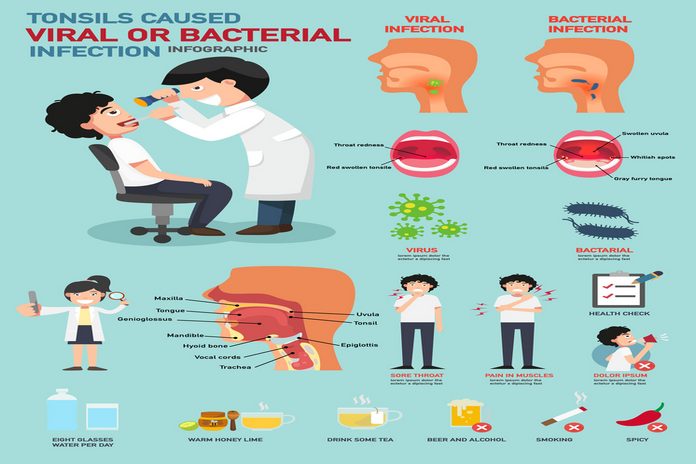
What Causes Tonsillitis?
A healthy set of tonsils is your first line of defense to prevent infections. White blood cells, produced by tonsils, are crucial to fighting infections. Viruses and bacteria entering your body through the mouth and nose are killed by the tonsils. Although tonsils help keep away pathogens, they are also at risk for infection by those very pathogens. (4)
Tonsillitis can be caused by viruses, such as the common cold. Other possible causes include bacterial infections, such as strep throat.
Viral tonsillitis:
Up to 70 percent of tonsillitis cases are caused by a virus such as;
Adenoviruses
Adenoviruses are responsible for causing epidemic respiratory illnesses in children and adults, commonly causing sore throat, runny nose and nasal congestion. These are multiple viruses that cause the common cold. These viruses are extremely common, and in fact are one of the most diverse types of virus. They are also one of the most difficult to eliminate, although they respond to medication quickly.
Adenoviruses cause a variety of diseases, some of which may be serious, including the common cold, the flu and pneumonia. They are among the most common viruses known, with about 100 serotypes identified to date.
Adenoviruses can trigger tonsillitis, pharyngitis (also called sore throat), croup and other infections in susceptible people. Adenoviruses usually cause only mild tonsillitis.
Influenza virus
The influenza virus is believed to be the most common cause of tonsillitis in adults. Influenza is a contagious illness that spreads easily from person to person through coughing or sneezing. You can get the flu and tonsillitis by breathing in small particles of the virus.
Adults who have had this condition may have a sore throat, trouble swallowing, and fever for about a week. They often feel very tired and may have muscle aches. In some cases, the condition may cause you to become dehydrated and have a fever, which can further lead to inflammation in your throat and tonsils.
Epstein-Barr virus
Epstein-Barr virus is a member of the herpesvirus family, and is the primary cause of infectious mononucleosis. This is a common cause of infectious mononucleosis and can also cause other diseases, including: tonsillitis, croup, glandular fever and certain types of cancer.
It is a highly contagious virus that can be spread by saliva and blood. Most healthy people will not develop symptoms if they are exposed to the virus, but Epstein-Barr virus infection can sometimes lead to life-threatening complications in those who have compromised immune systems. In most cases, the body’s immune system keeps EBV from causing other problems. However, EBV can reactivate later in life, causing tumors called lymphoproliferative diseases.
Parainfluenza viruses
Parainfluenza viruses are respiratory tract pathogens, primarily affecting children. Upwards of 20 million people in the U.S. annually suffer with this virus, and ~1% of them become hospitalized. The parainfluenza viruses are also known to cause outbreaks at daycares and preschools because they are highly contagious.
Parainfluenza viruses are a large family of viruses that cause cold-like symptoms, tonsillitis, and pharyngoconjunctival fever (PCF). They spread through close contact, such as when you kiss someone or share food or drink with an infected person. The virus can cause fever and a sore throat to develop after 1-2 weeks of being infected. In rare instances, it can lead to pneumonia and meningitis in young children.
Enteroviruses
Enteroviruses are one of the most common causes of viral tonsillitis. These viruses are contagious and can spread through direct contact with someone, who is infected or when droplets containing the virus (like the spray from a sneeze) is inhaled.
Enteroviruses are a widespread group of viruses belonging to the picornavirus family. Enteroviruses cause a wide variety of diseases, some of these include the common cold, croup, influenza, mumps and hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Herpes simplex virus
A less-common cause of acute tonsillitis is the Herpes simplex virus (HSV), it usually incubates for 2-6 days before symptoms appear. HSV is a herpes virus, an infection caused by varicella zoster virus that can trigger several different illnesses.
Bacterial causes
Most tonsil infections are caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. Occasionally, tonsillitis can be caused by another bacterial pathogen, including:
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of bacterial tonsillitis, as well as food poisoning and skin infections. It’s a staph bacteria that can cause severe throat pain after eating, and it is also responsible for causing ear infections. This bacteria is usually transmitted to people through coughing, sneezing and touching contaminated surfaces, as well as sharing utensils and food with people who have it.
It usually causes high grade fever, sore throat, and formation of pus (white colored) on the tonsils. It is most commonly treated with antibiotics such as methicillin, amoxicillin and levofloxacin. However, due to increased incidence of antibiotic resistance, some countries are also reporting methicillin-resistant staph tonsillitis.
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Mycoplasma pneumonia, or MP, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It can cause mild to severe disease in children and adults. Over 1 million people get sick from MP each year, with about 50 percent of those cases being diagnosed in children under age 18. It can spread through airborne droplets released into your surroundings when someone coughs or sneezes.
Mycoplasma pneumonia is a contagious bacterial infection that causes respiratory illnesses, including common cold, tonsillitis, and pneumonia. It is a member of the bacteria family that causes illness by invading the body’s epithelial cells (the cells that line your nose and throat). These are the smallest known form of life, so small they can only be seen with an electron microscope. Most people who catch mycoplasma do so from exposure to infected people coughing or sneezing around them.
Chlamydia pneumonia
Chlamydia pneumonia is one of the most common bacterial infections of the respiratory tract. It’s an airborne disease that can be spread through anyone who breathes in infected droplets from the coughs, sneezes and breaths of an infected person.
Chlamydia pneumonia causes respiratory tract infections – including tonsillitis- caused by the bacterium Chlamydia pneumoniae. It produces an acute inflammation of the upper respiratory tract and can be fatal in some cases. This bacteria is a common cause of chronic sinusitis and tonsillitis.
