Brain Scanning
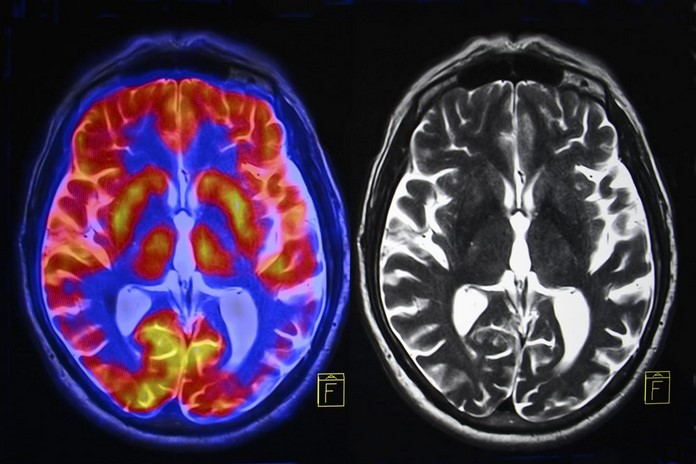
The doctors carry out brain scans to reveal the exact cause and area of degeneration in the brain tissues and some of these scans include positron emission tomography (PET) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and computed tomography (CT) scan. The detailed scanning of the brain allows the doctor to also identify the possible causes of some other symptoms that the patient is having.
The medical specialists conduct these diagnostic tests repeatedly to gain more information about how the cognitive functions and memory of the person is changing with time. The brain scans specifically aid in diagnosing other possible causes of memory loss such as tumor, stroke, sleep disturbances, Parkinson’s disease, an infection, side effect of a medication, or a vascular dementia. However, it is possible to reverse the symptoms of some of these conditions and treat the patients in the best way. People having memory loss issues must visit their doctor at least every 6 months or in a year to rule out if they are suffering from Alzheimer’s disease or not.
It is quite necessary to consider that certain patients only get a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease after they are dead, as the examination of the brain tissues link with clinical measures of degenerative brain cells in an autopsy report. On occasions, certain biomarkers i.e., that measure what is going on inside the body are better options for getting an accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. If your general physician or a primary care doctor suspects the possibility of Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment (MIC), then they refer you to a specialist who performs detailed diagnostic tests or do further assessment. Some of these specialists include:
- Geriatric psychiatrists: Geriatric psychiatrists are those who have the expertise in the emotional and mental health problems specifically of older adults and can better evaluate the memory and thinking issues.
- Geriatricians: Geriatricians are the specialists who are responsible for managing the health and care for older adults. A geriatrician knows much better than a general physician that how the body changes with aging and whether a certain patient’s symptoms point out towards a serious problem or not.
- Neurologists: Neurologists are the ones who have the specialization of any abnormalities of the central nervous system and the brain. Neurologists are able to review and conduct brain scans to rule out the possibility of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Neuropsychologists: Neuropsychologists specialize in conducting brain tests of thinking, problem solving, spatial awareness, and memory.
