Astigmatism causes
A common vision problem, astigmatism can cause blurred or distorted vision, which makes it difficult to see clearly. When the cornea (the transparent front layer) or the lens (inner part of the eye related to focusing of the light) are shaped differently, the eye cannot focus properly and leads to astigmatism. (3)
An irregular cornea or lens causes astigmatism. As a result of this abnormal shape, light enters the eye differently, causing an inability to focus and a refractive error. Astigmatism is a complex condition that has no definitive cause. The disease is primarily genetic, but a number of hours spent playing video games has been associated with severe astigmatism among children between 7 and 9 years old.
Astigmatism may be caused by:
- Genetics
- Eye injury
- Eye surgery
- Corneal diseases such as keratoconus
Genetics
A large part of this condition has to do with genetics. Refractive errors cause distortion in vision when the cornea forms an oval-like shape instead of the round shape it’s supposed to have. It is possible that your children will inherit it if you have a family history of it. Children may be born with astigmatism, which is why it’s important to have them undergo eye examinations early on to detect and treat any irregularities.
Researchers have reported that the risk of developing astigmatism doubles in first-degree relatives of astigmatism. Astigmatism is heritable in approximately 60% of families and twin studies, suggesting a significant genetic component.
Eye Injury
Besides genetics, environmental and dietary factors also contribute to the development of this condition. An eye injury can also result in astigmatism. Blunt trauma is one example. The chances of getting astigmatism are highest when injury occurs with sharp and small objects. The cornea can develop scarring when pressure is applied to the eyelid or if a blunt trauma occurs – leading to astigmatism.
Eye Surgery
Some eye surgeries, such as those for cataracts, can result in residual astigmatism. Surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) occurs when an incision is made to perform cataract surgery. SIA can be determined by comparing preoperative and postoperative angles of the cornea using different equations. The amount of scarring and fibrosis that occurs during this process can be affected by factors like the patient’s healing ability and response.
Refractive Error
Incoming light is bent incorrectly by a cornea or lens with mismatched curves, like an egg. These images overlap, resulting in blurred vision. When the cornea or lens has a specific angulation or curve in one direction than the other, it is called astigmatism. Depending on the structure that has mismatched curves, you will have different types of astigmatism.
Astigmatism can occur alongside myopia and hyperopia as a refractive error. During an eye examination, refraction can determine the degree of astigmatism. Refractions help determine if regular eyeglasses or contact lenses can improve or correct both close-up and distance vision by testing with different lenses.
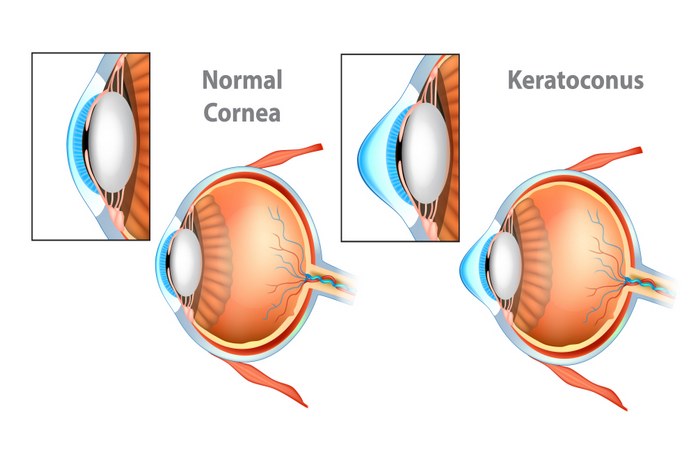
Keratoconus
In keratoconus, the cornea gradually thins out, resulting in a cone-shaped cornea and blurred vision. The smooth surface of the cornea becomes wrapped in this rare eye disease and degenerative disorder – that further leads to astigmatism. In the long term, it may even lead to blindness since it cannot be corrected with glasses. Corneal transplants can provide a possible cure. Corneal transplants are generally uncommon.
Uncertainty surrounds the cause of keratoconus. Approximately ten percent of keratoconus sufferers have a parent who also has the condition. Patients with Down syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, asthma, retinitis pigmentosa, and hay fever are more likely to develop the condition.
According to medical researchers, an enzyme imbalance within the cornea makes it vulnerable to damage by free radicals, which leads to corneal tissue deterioration and bulging.
