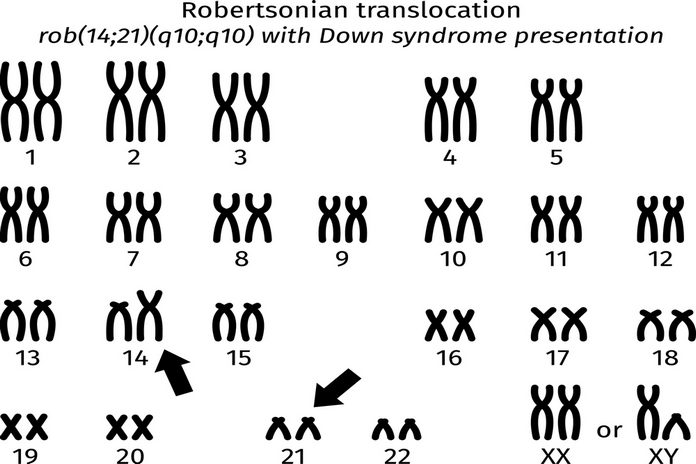
Translocation Down syndrome
The complication of genetic science increases even more here. Translocation Down syndrome occurs when a partial or an extra full copy of the 21st chromosome is present — as it occurs in trisomy 21. But in these patients, the partial or extra full 21st chromosome gets attached to one of the other 23 pairs of chromosomes—usually, chromosome 14. The presence of the partial or extra full chromosome 21 leads to the characteristics of Down syndrome. So usually, a person with translocation Down syndrome has the normal 46 chromosomes, but one of them gets bound to an additional 21st chromosome. Only 3 to 4 percent of patients have this type of Down syndrome.