Diagnosis and Progression of Sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis can be difficult to diagnose, as its symptoms are similar to other conditions such as arthritis and spinal stenosis. There are several methods of diagnosis, including blood tests, X-rays, and MRI scans.
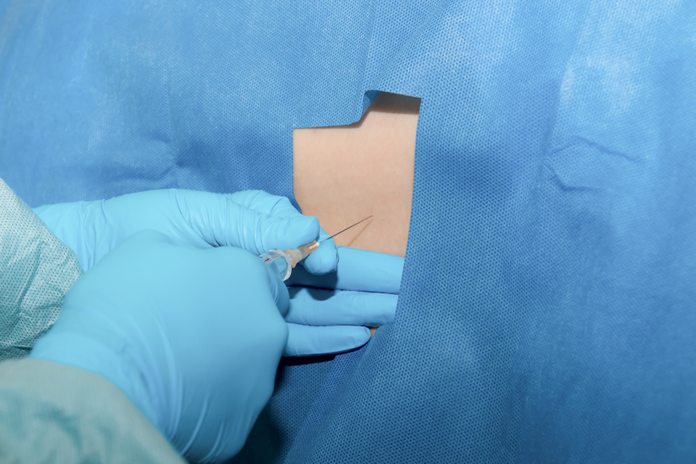
Anesthetic injections
Anesthetic injections may be used to help diagnose sacroiliitis. When an anesthetic is injected into the space around the spine, it numbs the nerves in that area. If this procedure relieves pain when pressure is applied to the affected area, it suggests that you have sacroiliitis.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests such as an X-rays, MRI or CT scan may be used to help confirm a diagnosis of sacroiliitis. These tests can help your doctor see how severe your condition is and whether there is any damage to the bones or tissues in your joint.
X-Rays – X-rays are an important tool for diagnosing sacroiliitis, as they can help identify inflammation or damage to the sacroiliac joints. In some cases, x-rays may also show signs of other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as arthritis or spinal stenosis. If x-rays suggest that you might have sacroiliitis, your doctor will likely order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis.
MRI – MRI is a common diagnostic tool used to identify sacroiliitis, a condition that affects the sacroiliac joint. The MRI will show inflammation and damage to the joint and surrounding tissues. This information can help your doctor determine the best treatment plan for you.
Ultrasound – Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It can be used to examine various parts of the body, including the joints. In cases of suspected sacroiliitis, ultrasound may be used to assess the health of the sacroiliac joint and look for signs of inflammation or damage.
CT scan – A CT scan is often used to diagnose sacroiliitis. A CT scan uses strong X-rays to create a three-dimensional image of the body. This image can help your doctor determine if you have sacroiliitis and how severe it is.
Blood tests
Sacroiliitis is typically diagnosed through a physical exam and by ruling out other conditions that could be causing the symptoms. However, blood tests may also be used to help diagnose sacroiliitis.
ESR – The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is often elevated in people with sacroiliitis. This test measures how quickly red blood cells fall to the bottom of a test tube. An increase in ESR can be a sign of inflammation.
CRP – The C-reactive protein (CRP) is another marker of inflammation that may be elevated in people with sacroiliitis.
