Imaging Tests and other Tests
Most cases of wrist pain do not require very specialized imaging tests. The first-line imaging modality is radiography, and some patients may not even need imaging tests at all. A radiography will provide a clear view of the bony structures, and doctors will be able to evaluate the joint space width and other essential parameters. When a misalignment is found, a ligament tear can be diagnosed, and if you don’t treat the condition, it can progress to osteoarthritis.
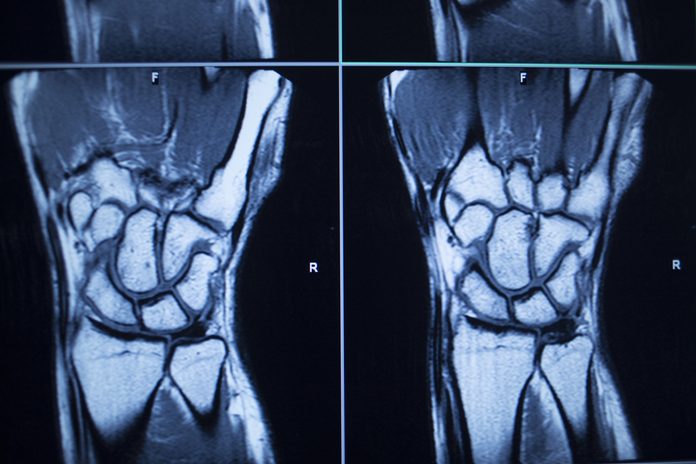
When soft tissue appears to be the problem, sometimes doctors would require additional tests such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. The latter can diagnose synovial cysts, tendon injuries, and synovial thickening without high expenses. However, an ultrasound depends on the operator and may not be effective in some cases.
Other tests can also come in handy, especially if your doctor suspects a systemic disease. For example:
- Septic arthritis will give you fever and a high white blood cell count.
- Your rheumatoid factor and other blood markers can be positive in rheumatoid arthritis.

