Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis
The diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy mostly involves the confirmation of blood sugar levels indicating diabetes and a series of tests by an eye specialist. When a patient with symptoms of diabetic retinopathy visits an ophthalmologist, the doctor will inquire about the medication history and prior vision issues. The doctor uses a specialized instrument known as an ophthalmoscope to examine the eye. Following are the methods in practice to diagnose diabetic retinopathy in a patient:
- Dilated eye examination
An eye specialist or ophthalmologist will diagnose the condition of diabetic retinopathy by doing a comprehensive dilated eye examination on a patient. The doctor will put drops in the patient’s eye to dilate the pupil to allow the specialist to look via a special lens inside the eye to diagnose diabetic retinopathy. The special eye drops widen the pupils of the eye to create a better inside view of the eyes. The drops can result in the blurring of a person’s close vision until they wear off after several hours. During the eye exam, the doctor will search for abnormalities in the internal and external areas of the eye.
- Fluorescein angiography
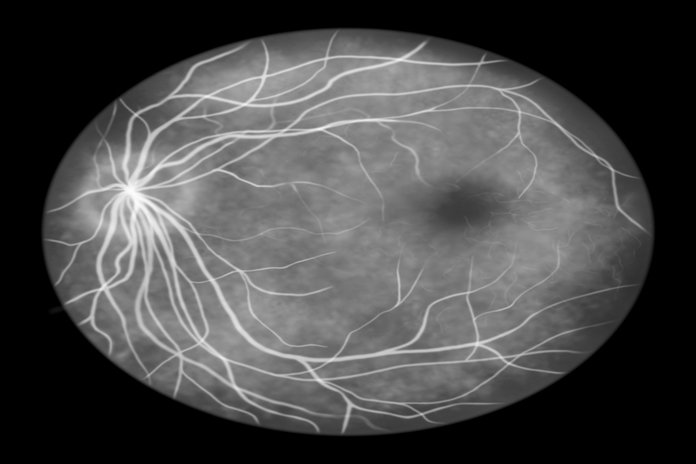
After the eyes dilate due to the special eye drops, the eye specialist injects a dye into a vein near the arm of the patient. In addition, the eye specialist takes pictures as a special dye circulates through the blood vessels inside the eyes. The images of the eye blood vessels can pinpoint the blood vessels that suffer from breakage, leakage, and tearing. Fluorescein angiography helps the doctor to see what is actually happening with the blood vessels present in the retina of the eye. There is utilization of a special yellow dye known as fluorescein in fluorescein angiography which the doctor injects into a vein usually in the arm. The dye tends to travel through the blood vessels and a special camera captures pictures of the retina. The scanning shows if any blood vessels are suffering from any blockage or leakage of any kind in the retina. The results of fluorescein angiography also reveals if there is any growth of abnormal, new blood vessels in the cavity around the retina.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Scanning images that develop from the test of optical coherence tomography (OCT) supply cross-sectional pictures of the retina that indicate the thickness of the retina. The OCT will help to determine how much liquid if any leaks into the retinal tissues. In later stages, the OCT exams can be helpful to monitor how treatment is functional. The doctor might do optical coherence tomography (OCT) to look keenly at the retina. A machine helps to scan the retina and supplies detailed images of the blood vessel’s thickness. The OCT test helps the eye specialist to find and gauge the swelling of the macula in the eye. The doctors nowadays prefer to use optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an advanced technique as compared to fluorescein angiography and does not require any injection of dye into the body to look at the blood vessels. (4)
