Arthritis is the most commonly occurring disease of joints, which can affect the all joints like hands as well as knees and hips. Knee arthritis usually affects joint functionality that leads to severe knee pain and even disability as it progresses. There are various stages of knee osteoarthritis (OA), starting from 0 which is assigned to a normal, healthy knee and leading to the advanced stage 4 that is chronic OA. [1]The Center for Disease Control and Prevention says that the number of individuals suffering from knee arthritis is gradually rising, with approximately 1 in 2 people are at risk of developing symptomatic knee OA in their lifetime which has a significant impact on their health, work productivity and economic costs.
Knee pain is easily identifiable through common and diagnostics symptoms. Some individuals who suffer from severe osteoarthritis knee pain may only show a little change on x-ray, so it is very important to concentrate on the signs and symptoms, rather than just the x-ray reports. Here is a look at the different stages of the knee arthritis – ranging from normal, minor, mild, and severe stages.
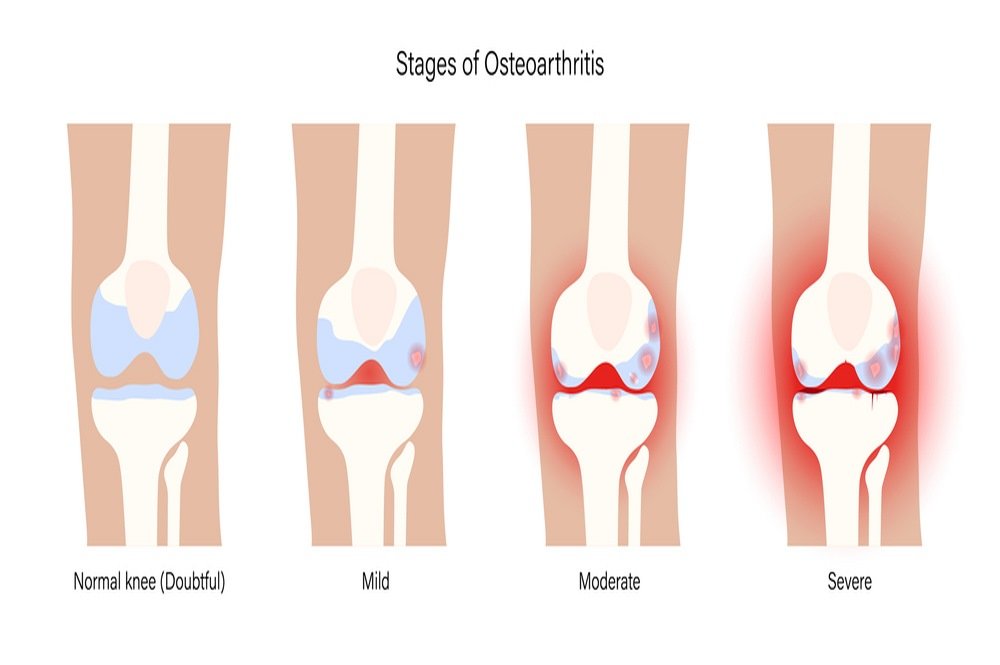
- Stage 0 – Normal
When the knee shows no signs or symptoms of osteoarthritis, it is classified as stage 0, which is termed as a normal knee, with no sign of impairment or joint damage.
- Stage 1 – Minor
In this stage patients will develop very minor bone spur growths and wear & tear at the end of the knee joints. The patient usually does not feel any pain or discomfort.
- Stage 2 – Mild
In Stage 2, X-rays or diagnostic images of knee joints will show bone spur growth, and though the area around the bones appear normal, people will begin experiencing various symptoms of joint pain. Typically, the space between and around the knee joints will feel rigid and uncomfortable, particularly after rising in the morning, when sitting for an extended period, or after a workout. Though the soft tissues and cartilage remains at a same healthy size, there is a breakdown of the cartilage matrix due to an increased production of several enzymes, such as metalloproteinases.
- Stage 4 – Severe
It is considered to be a severe stage. The joint space between the bones are reduced, causing the wear to a cartilage, making the joint stiff. The breakdown of cartilage causes a chronic inflammatory response, thus synovial fluid is decreased that causes friction, discomfort and greater pain when walking or moving the joint.

