Risk factors for osteopenia consist of
- Smoking
- Family medical history of having osteoporosis
- Being thin
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Low-impact bone fracture previously
- Asian descent
- In women, low estrogen level
- Corticosteroid use
- Lower testosterone level in men
- Malabsorption situations such as celiac disease
- And alcohol intake on a daily basis
Osteopenia is curable with adequate vitamin D and calcium intake, not smoking, exercising daily, lowering corticosteroid usage, and avoiding alcohol. Osteopenia mostly leads to no symptoms at all and is sometimes not detected without performing a bone density test. When osteopenia does show symptoms, it might consist of weakness in a specific area where the bone fracture occurred previously and localized bone pain. Even though such a condition might present no symptoms initially, some factors that might show towards such condition are:
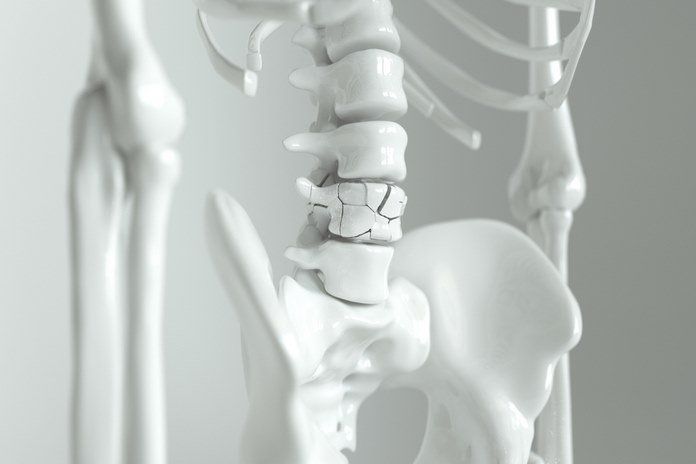
- Weakness in the bone
- Localized pain where bone get affected
- Bone fractures might occur in severe cases without any pain
One of the most difficult parts of osteoporosis is that it is sometimes considered a silent disorder in its starting stages. You might not realize that you are having such a condition unless you experience breaking a bone or fracture. You might be experiencing bone loss gradually by the time without any evidence that it is occurring. The key minerals and diet high in vitamin D and daily exercise or any other physical activity will aid in keeping your bones strong and reducing the risk of bone fractures.
Because of such, it is essential to practice other bone-healthy behaviors, consisting of these outlined in such a Patient guide, therefore even if you do not experience any symptoms of osteopenia. You might lower the risk factor for such condition and prepare yourself better if you eventually do have osteoporosis by doing proactive steps such as:
- Form an osteopenia prevention exercises: It might lead to weight-bearing exercises and strength training
- Enhance your diet by considering vitamin D, calcium, and some other friendly nutrients and minerals
- Visit your doctor and ask questions regarding osteoporosis. However, some alarming signs consist of the low density of bone and an increased chance of having osteoporosis. If you have any of these symptoms or situations, talk or visit your healthcare provider regarding the step you might take to protect and strengthen your bones
- Low bone density: Osteopenia, sometimes also known as low bone density, refers to a situation in which bone density is less than the average but not enough to be considered osteoporosis. The low density of bone does not make sure that you will experience osteopenia in the future.
