Prediabetes Diagnosis
Diabetes is a measurement of sugar levels in your bloodstream. Physicians examine this in two various ways:
- An A1C blood test
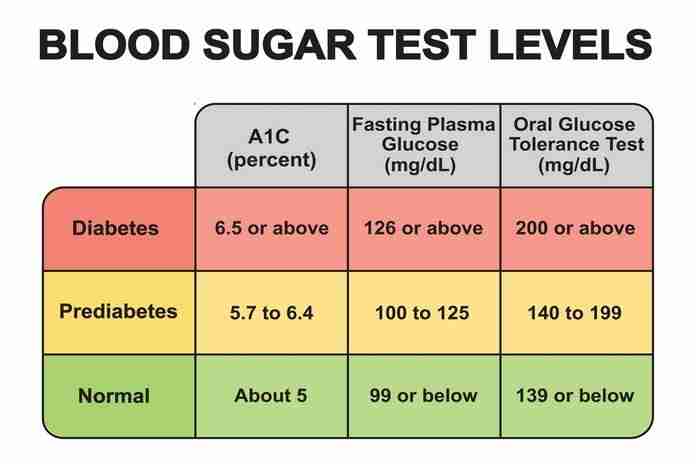
The test of hbA1C or A1C is a non-fasting blood test that examines the normal amount of sugar in your blood by the time of three months and is measured in percentages. So, a normal percentage is less than 5.7% and 6.4% recommend prediabetes. Anything that is increasing more than 6.5% shows that an individual has diabetes.
- A standard blood glucose test
Therefore, this needs you to fast prior to a blood test, so your endocrinologist or PCP might check the level of sugar in the bloodstream at any given time. Normally, fasting sugar levels must be 99 mg/dL or reduced. Therefore, if the fasting blood sugar levels are between 100 and 125 mg/dL, it must be considered prediabetes. While, a reading is also increasing than 126 mg/dL shows diabetes.
Normal range
So, the test indicates the average blood glucose level for the past three months. This test measures the blood glucose percentage attached to the oxygen carrying protein present in the red blood cells known as hemoglobin. The increasing blood sugar level the more your hemoglobin will have attaching glucose.
Generally,
- An A1C level is less than 5.7% is considering normal
- While, an A1C level between 5.7% and 6.4% is considering prediabetes
- An A1C level of 6.5% or increasing on two different tests shows diabetes type 2
Therefore, some conditions might make the A1C test show inaccurate results such as if you are pregnant or have a common form of hemoglobin.
Fasting blood sugar test
However, the blood sample is taken after you are fasting for almost eight hours or overnight.
- A fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or increasing shows diabetes type 2
