Types Of Tonsillitis
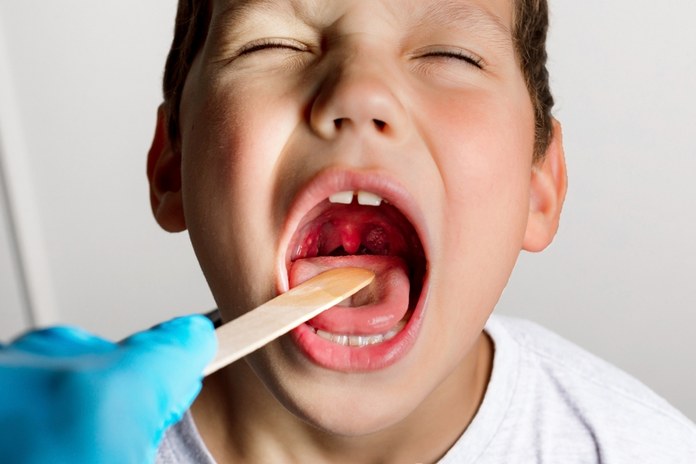
Tonsillitis is common in children, but can occur in adults as well. There are three types of tonsillitis: acute, recurrent and chronic (acute on chronic is another one). (2)
By producing antibodies, both tonsils and adenoids guard the throat against disease germs that enter from the nose or mouth. Consequently, these lymph nodes are also more prone to inflammation and infection caused by bacteria and viruses.
- Acute Tonsillitis – Either a virus or bacteria causes it. It is the most severe form of tonsillitis that causes sore throat and high grade fever in children.
- Recurring Tonsillitis – If there are up to seven episodes of tonsillitis or throat infections in a year or three in each year of three consecutive years, it is referred to as recurrent tonsillitis. Cessation of the antibiotic in such cases can lead to another infection within a few weeks.
- Chronic Tonsillitis – As its name suggests, chronic tonsillitis occurs when there is a constant sore throat, persistent tender cervical nodes, or bad breath secondary to tonsillitis infection.
- Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA) or Quinsy – When a tonsillitis infection goes untreated, a peritonsillar abscess develops lateral to the tonsil area. The peritonsillar region becomes inflamed or swollen. Staphylococci, Fusobacterium necrophorum, haemophilus influenzae, and streptococci are the most common pathogens. There are no viruses involved. Symptoms include severe throat pain, fever, altered voice quality, drooling of saliva, difficulty opening the mouth, and foul breath.
- Tonsillar Hypertrophy – Tonsil enlargement accompanied by difficulty speaking, snoring, and swallowing difficulty.
