Sacroiliitis
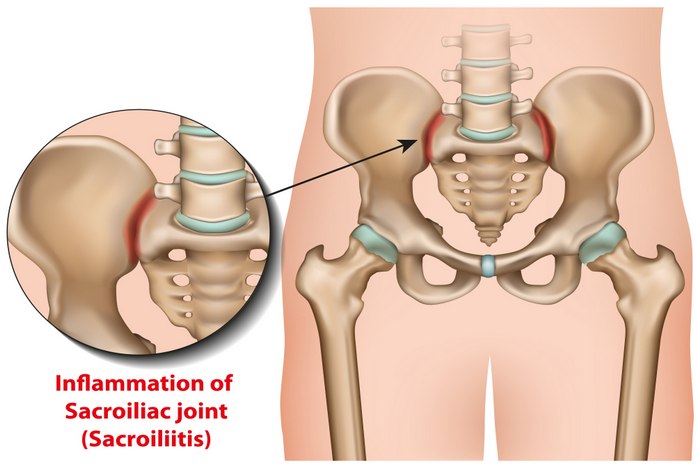
Sacroiliitis is a condition that affects the sacroiliac joint, which is located where the spine meets the pelvis. Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the lower back and hips. The condition may also cause inflammation in the joint and surrounding tissues. Sacroiliitis is most often caused by an injury or infection to the joint. However, other conditions such as arthritis, lupus, and ankylosing spondylitis can also lead to sacroiliitis.
The condition is relatively common, affecting about 1 in 100 people. It can occur at any age, but is most often seen in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. Women are more likely to develop sacroiliitis than men. There is no known cause of sacroiliitis, but it may be related to genetics or an infection. Symptoms of sacroiliitis include pain in the lower back and hips, stiffness in the joints, inflammation around the joint, and a decreased range of motion.
Treatment for sacroiliitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and pain. We will discuss the specific treatment options in the treatment section of this blog.
Pathophysiology
Sacroiliitis is a condition that results when the sacroiliac joints become inflamed. The sacroiliac joints are the two joints located at the base of the spine, where the spine meets the pelvis. Sacroiliitis can cause pain in the lower back and buttocks, and can also lead to difficulty walking.
Pathophysiology of sacroiliitis is still not fully understood, and there are many factors that could contribute to its development. Some of the most common include: genetics, infections, autoimmune conditions, and injuries. However, the cause is often difficult to determine, as it can be multifactorial. Patients with sacroiliitis may have an increased risk of developing other autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
One of the main theories on the pathogenesis of sacroiliitis is that it is an autoimmune condition. In this case, the body’s own immune system attacks the joints in the lower back. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as infections or exposure to environmental toxins.
Another theory is that sacroiliitis is caused by inflammation in the spine. This can be due to a number of factors, such as arthritis or an injury. When this inflammation occurs, it can cause pain and stiffness in the lower back region.
Genetics
While the cause of sacroiliitis is not always clear, it is believed that genetics may play a role in its development. Studies have shown that people who have a family history of sacroiliitis are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Additionally, research has indicated that certain genes may be associated with an increased risk of developing sacroiliitis. These genes are thought to affect the body’s ability to process inflammation, which could contribute to the development of this condition.
Further study is needed to determine exactly how genetics contributes to the pathophysiology of sacroiliitis, but these early findings suggest that it may be a significant factor.
Infections
One of the key factors in the pathophysiology of sacroiliitis is infection. Infections can cause inflammation and damage to the tissues around the joint. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and other symptoms of sacroiliitis. In addition to causing inflammation, infections can also increase the risk of developing other complications related to sacroiliitis.
Autoimmune
Sacroiliitis is a form of inflammatory arthritis that affects the sacroiliac joints, located where the spine meets the pelvis. The cause of sacroiliitis is unknown in many cases, but it is believed that autoimmune factors may play a role in its pathophysiology.
Studies have shown that patients with sacroiliitis have higher levels of certain antibodies that are associated with autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. This suggests that autoimmune mechanisms may be involved in the development of sacroiliitis.
Further research is needed to determine the role of autoimmune factors in sacroiliitis, but these findings could lead to new treatments for this condition.
Injuries
Sacroiliitis can be caused by a number of factors, including injuries to the area, autoimmune diseases, and infections. When these factors cause inflammation in the sacroiliac joints, they also can disrupt the normal function of those joints. This can lead to pain and stiffness in the lower back and hips, as well as difficulty with movement.

