Diabetes Diagnosis: Tests Used to Detect Diabetes
The earlier you have your diagnosis with diabetes, the better you can begin the treatment. Find out either you should have tested, and have more information regarding the test your doctor might do. If you do not have a primary care specialist already, you better look for doctors in your area by the various tools present online. The weekly micro-lesson might empower you with the idea you require to make healthy variations for your diabetes. Easy and short tips to follow just for the week ahead. The following are the blood tests that provide aid to your healthcare giver diagnose type 1 diabetes:
- Blood glucose test: Your healthcare giver performs a blood glucose test to examine the sugar amount present in your blood. They might ask you to perform a random test (without fasting) and then a fasting test (no drink or food for almost eight hour prior to the test).
- Antibody test: A blood test examines autoantibodies to check if you are having type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Autoantibodies are the proteins that fight against your own body tissues mistakenly. The occurrence of certain autoantibodies means you have Type 1 diabetes. Autoantibodies typically don’t occur in type 2 diabetes.
- Glycosylated hemoglobin test (A1c): If the blood glucose test results show that you have type 1 diabetes, your healthcare giver might do an A1c test. This test measures your approximate blood sugar level for almost three months.
Anyone who is experiencing the symptoms of diabetes or is at higher risk for the disease must get tested. Women who are tested routinely for gestational diabetes during their third or second pregnancy trimesters. Doctors utilize such blood tests that are in the following to check diabetes and prediabetes:
-
- The fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test determines the blood sugar after the fasting of 8 hours.
- The A1C test gives a snapshot of the blood sugar level by the previous 3 months.
For the diagnosis, the doctor will do a test of your blood sugar level during the 24th and 28th weeks of the pregnancy. During the glucose challenge test, the blood sugar checks an hour after you drink a sugary fluid. During the 3 hour glucose tolerance test, the blood sugar is being checked post you fast overnight and then take a sugary liquid.
If an individual has symptoms that might show type 1 diabetes, a doctor will perform blood tests. A random plasma glucose test might indicate blood glucose levels at some specific time. An A1C test also measures blood glucose levels by the time of 3 months, which might indicate how long levels have been increasing. These tests might show if type 1 diabetes is occurring, but an individual will require more tests to detect if it’s type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Healthcare professionals might do a blood test to search for autoantibodies that are most occurring in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. If your doctors assume you have type 1 diabetes, they will show your blood sugar levels. They might test your urine for chemicals or glucose present in your body forms when you don’t have sufficient insulin.
- Normal range
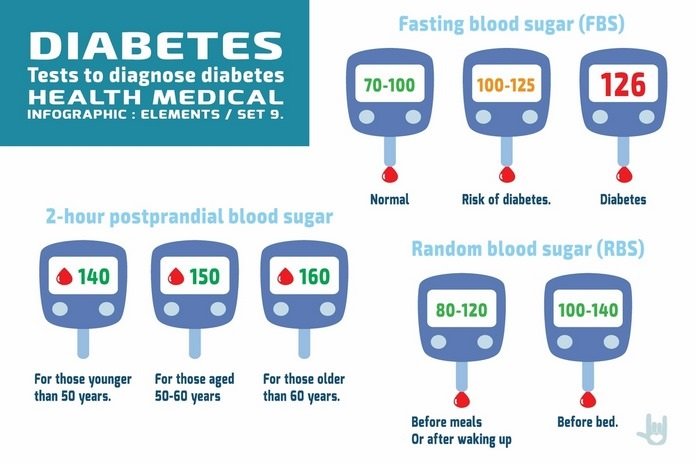
The blood test shows the average blood sugar level for almost two to three months. It measures the blood sugar percentage attached to the oxygen carrying protein present in the red blood cells (known as hemoglobin). The increasing blood sugar levels, the more hemoglobin you will need with the sugar. An A1C range of 6.5 percent or more than two separate tests show type 1 diabetes. There are few kinds of blood sugar test in the following:
- Random blood sugar test:
A blood sample taken at different times and might be confirmed by repetitive tests. Blood sugar values are defined in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Other than when you last ate, a random blood sugar level 11.1 mmol/L or 200 mg/dL or higher recommends diabetes type 1, significantly when couples with any of the symptoms or signs of diabetes such as extreme thirst and frequent urination.
- Fasting blood sugar test
A sample of blood will be taken just after the night fasting. A fasting blood sugar level lower than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is moderate. A fasting blood sugar level from the range of 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) is considered prediabetes. If it is 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) or increasing on two different tests, then you have type 1 diabetes. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, your doctor might also run blood tests to examine for autoantibodies that are most occurring in type 1 and type 2 diabetes when its diagnosis is not certain. (6)
