Type 1 Diabetes Complications
Type 1 diabetes complication and if you do not sustain it properly, there is complication both long-term and short-term. If you do not manage them properly is a significant statement that means you carefully keep an eye on managing blood glucose levels. You can prevent or stave off the long-term and short-term complications. And if you have developed type 1 diabetes complications already, then start controlling your blood sugar levels that will be helpful in preventing such symptoms and inhibiting further damage. Diabetes complications are related to bad blood glucose control, so you must carefully work with you consultant and diabetes team to manage your blood sugar level correctly (or the child’s blood sugar level).
Short-term diabetes complications
Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia is low blood sugar level. It forms when there is a lot of insulin that means that you have given or taken too much insulin or that you have not planned insulin around exercise or meals properly. Other possible reasons for hypoglycemia consist of certain medications: aspirin for instance, reduces the blood glucose level if you attain a dose more than 81 mg and alcohol (alcohol makes your liver from secreting glucose. There are three levels of hypoglycemia, relying on how the blood glucose level has reduced: severe, mild and moderate. If you cure hypoglycemia when it is in moderate or mild stages, then you might prevent far more severe problems such as severe hypoglycemia might lead to coma or even death (even though quite rarely).
The symptoms and signs of low blood glucose are normally simple to recognize:
- Anxiety
- Rapid heartbeat
- Headache
- Sleepiness
- Sweating
- Paleness of skin
- Numbness in toes, fingers and lips
- Confusion
- Slurred speech
- Frequent urination
- Cold skin
- Weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Extreme thirstiness
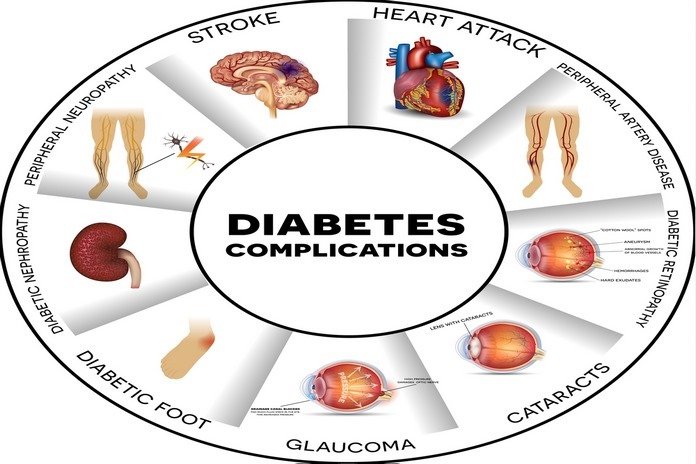
For further information regarding hypoglycemia and how to cure it. If you are a parent with a child who has type 1 diabetes, visit your healthcare provider. By that time, type 1 diabetes complications might affect major organs in the body, consisting of blood vessels, eyes, nerves, heart and kidneys. Sustaining a normal blood sugar level might lower the chance of various complications dramatically. Type 1 diabetes might be disabling or even lead to life threatening conditions eventually.
- Blood vessel and heart disease
Type 1 diabetes might raise the risk of several cardiovascular problems, consisting of stroke, coronary artery disease along with chest pain (angina), high blood pressure, heart attack and narrowing of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
The kidneys consist of millions of minute blood vessel clusters that remove the waste from your blood. Type 1 diabetes can harm this delicate system of filtration. Extreme damage might lead to irreversible end stage kidney disease or even kidney failure that needs kidney transplant or dialysis.
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Excessive sugar might injure the walls of the small blood vessels (capillaries) that provide nourishment to your nerves, particularly in the legs. This might lead to numbness, tingling, pain or burning that typically starts at the tips of the fingers or toes and slowly spreads upward. Poorly controlled blood sugar can lead you to lose all the sense of feeling in the limbs that are affected eventually. The damage to the nerves might affect the gastrointestinal tract that lead to the several problems such as diarrhea, nausea, constipation or vomiting. In men, erectile dysfunction might be a problem.
- Eye damage
Type 1 diabetes might harm the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic retinopathy), significantly leading to blindness. Diabetes also raises the chance of other severe vision conditions like glaucoma and cataracts.
- Mouth and skin conditions
Type 1 diabetes might leave you more prior to infections of the mouth and skin, consisting of fungal and bacterial infections. Dry mouth or gum diseases also are more likely to develop.
- Foot damage
Nerve disorder in the feet or bad blood flow to the feet raises the chance of several foot complications. Left untreated blisters and cuts might become severe infections that might require toes ultimately, leg or foot amputation.
- Pregnancy complications
High blood sugar levels might be severe for both baby and the mother. The chance of stillbirth, miscarriage and birth defects rises when type 1 diabetes is not properly controlled. For the mother, type 1 diabetes raises the susceptibility of diabetic ketoacidosis, pregnancy inducing high blood pressure, diabetic eye problems (retinopathy) and preeclampsia. High blood sugar harms the tissues and organs throughout the body. The increasing blood sugar is and the longer you will live with it, the higher risk for complications.
- Cardiovascular disease
Type 1 diabetes might put you at increasing risk of blood clots, cholesterol and high blood pressure as well. These might lead to heart attack, heart failure, chest pain and high blood pressure.
- Gum disease
The reduction of saliva, a lot of plaque and bad blood flow might also lead to mouth problems.
- Skin problems
Individuals having type 1 diabetes are more likely to have fungal or bacterial infections. Diabetes can also lead to rashes or blisters.
- Retinopathy
This eye disorder occurs in almost 80% of adults who are having type 1 diabetes for more than 15 years. It is quite rare prior to puberty, no matter how long you have had the disorder. To cure it and keep your eyesight sustainable, blood pressure, triglycerides and cholesterol.
- Bad blood flow
The hardening arteries and damaged nerves lead to a sensation of loss in and a reducing blood supply to the feet. This might increase the chance of injury and make it harder for wounds and open sores to heal. When it happens, you can lose a limb. Nerve damage might also lead to digestive conditions such as vomiting, nausea and diarrhea.
- Kidney disorder
Almost 20 to 30 percent of people having type 1 diabetes have a situation known as nephropathy. The risks go up by the time. It is more likely to indicate 15 to 25 years after the ongoing type 1 diabetes. It might lead to other severe conditions such as heart disease and kidney failure. (7)
