Bronchitis is a common lung condition that often develops from cold, flu or other respiratory tract infections. It is characterized by the inflammation of lower respiratory tract that includes bronchial tubes, bronchioles, and alveoli. Inflammation of the bronchial tree results in obstruction of the respiratory tract due to an increase in mucus production as well as a decrease in the oxygen carrying capacity of the lungs. Depending on the duration of inflammation, the bronchitis is further divided into acute and chronic bronchitis.
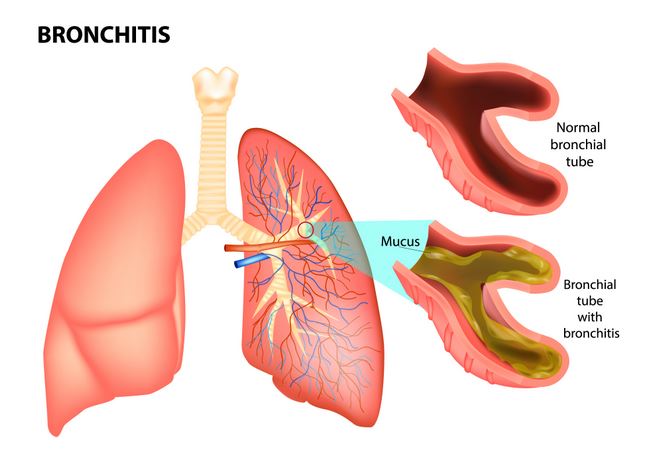
Also called a chest cold, acute bronchitis is a short-lived condition that usually resolves within one to two weeks. It doesn’t cause lasting effects, although a cough may linger for weeks. Chronic bronchitis is a more serious condition that causes repeated bouts of bronchitis and results from a constant irritation or inflammation of bronchial tree for more than a month. The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is active or passive smoking and a recent history of recurrent attacks of acute bronchitis. It is one of the conditions included in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The incidence of bronchitis and other lung infections is very high in America as well as around the globe. It most commonly affects adults and women. In 2016, approximately 8.9 million cases of acute bronchitis were registered in the United States alone. Out of them, nearly 55% of cases involved people over the age of 50. Globally, women have chronic bronchitis at almost double the rate of men.

