Causes of Ocular Migraine
There is no clear answer to what causes the Ocular Migraine but the scientists are still trying to figure it out. Although there are many theories, doctors believe it is caused due to spasms and lack of blood and oxygen supply to the retina or at the back of the eye. Whereas, some doctors believe that the problem in the visual cortex might be the reason behind migraine. (4)
Some factors that might cause spasm and in some cases cause ocular migraine are:
Disorders
Certain illnesses can also contribute to causing ocular migraine. In order to treat such a type of ocular migraine a person must first find a cure for the underlying illness.
- Lupus
Lupus is an autoimmune disease in which the white blood cells start attacking the body tissues. 70% of people suffer from neurological disorders due to lupus, ocular migraine being one of them. No clear answer has yet been discovered to why people with lupus suffer from migraine like headaches and ocular migraine, but a possible explanation can be, since the white cells start attacking the host body, the muscles and arteries around the eyes and retina undergo many changes, which causes ocular migraine. Lupus also contributes to people being photophobic, so the eyes and vision cortex being sensitive to light, make the patient more vulnerable towards ocular migraine.
- Hardening of the arteries
Sometimes due to clotting, not enough supply of blood reaches the brain, which results in ocular migraine. The most extreme complication can result in a stroke or a complete vision loss. This blocking might be due to thickening of the arteries i.e. CADASIL (Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy), which is a hereditary illness. During CADASIL the blood that flows from the heart to the brain is disrupted, which leads to less supply of the blood around the brain and areas around the eye causing Ocular Migraine.
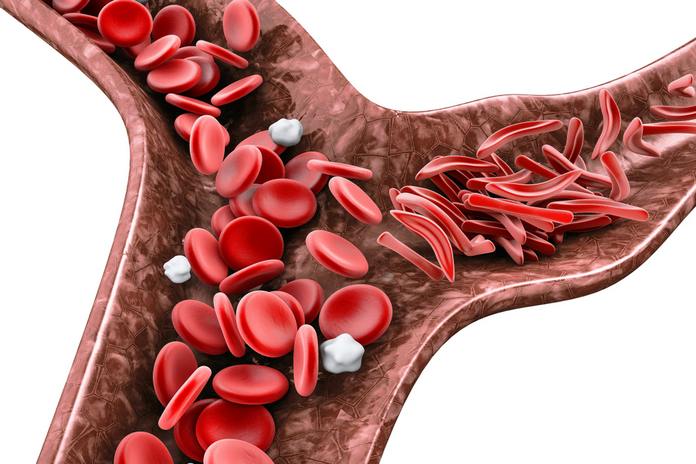
- Sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease is caused by a genetic mutation in the HBB gene, which changes the shape of the red blood into a sickle. This shape prevents the red blood from carrying the required amount of oxygen. Moreover, this shape also damages the cell membrane of the red blood cells resulting in premature destruction. This sickle shape of cells can easily block the arteries and capillaries and form clots around the eyes and brain until the arteries burst from increased pressure while damaging the vision cortex. The early cell death also makes the patient anemic, which further contributes to ocular migraine.
- Epilepsy
People with epilepsy are two times more likely to experience ocular migraines compared to some who don’t have epilepsy. In epilepsy the patient’s brain undergoes a sudden chemical change which causes a surge in the brain electrical signals. This abnormal brain activity affects different lobes of the brain controlling the vision. There are also some claims that migraine might be the reason behind epilepsy in some people, but no clear evidence has yet been found.
- Temporal arteritis
Temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell, is the disorder in which the arteries are damaged due to inflammation. Since the inflammation mostly occurs along the temples of the head it is called temporal arteritis. The inflammation damages the eye and optic nerve, increasing the pressure on the brain to see things clearly. This inflammation also results in less supply of blood and oxygen to the eye, which is the major cause behind vision problems, auras and ocular migraine.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid is an autoimmune disease in which the body starts producing antibodies that start attacking the healthy tissues of the body. This increased amount of antibodies can block the veins which prevent the blood from reaching the brain causing neurological disorders. These neurological disorders can cause ocular migraine
Genetics
Even though, both normal migraine and ocular migraine are different terms, doctors believe they might have the same genetic mutation involved. People having a strong family history with genetic mutations are more likely to experience migraine with an aura and severe symptoms and are diagnosed with migraine at an early age. In the light of the research performed by The Journal of Headache and Pain, the mutations in genes which result in TRESK, FASPS and CADASIL are some major causes behind ocular migraine and migraine with an aura.
Family history
People with a family history of ocular migraine are more likely to develop ocular migraine. According to a survey, the Ocular migraine and migraine with an aura are hereditary conditions. People with a family history with a hyper-excitable brain are more vulnerable to developing ocular migraine. The hyper-excitable brain is more sensitive towards senses, which disturbs the nervous and chemical signals causing an ocular migraine. According to a survey by the World Health Organization, 70% of all ocular migraine are hereditary.
Gender
Ocular migraine is more common in women than in men. This is because women tend to undergo more hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy and menopause as compared to men. Moreover, the menstrual cycle and hormonal changes happen early in females as compared to males.
Hormones
Hormones are responsible for sharing and transporting information between the brain and the body. According to a study, the hormonal changes in the body make the cells more sensitive, which causes ocular migraine. Before the menstruation cycle, the estrogen and progesterone levels fall which causes females to experience ocular migraine. Hormonal changes in male sex hormone i.e. testosterone is responsible for ocular migraine. Any rise and fall in the hormones can result in migraine.
Age
People in their early 30 and 40 are likely to develop ocular migraine. The symptoms of ocular migraine also start to get worse due to increasing age. A possible hypothesis for this is, due to increased age our body stops producing hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, which are responsible for controlling chemical changes in the brain. Any uncontrolled chemical change can cause the arteries and nerves to contract causing ocular migraine.
