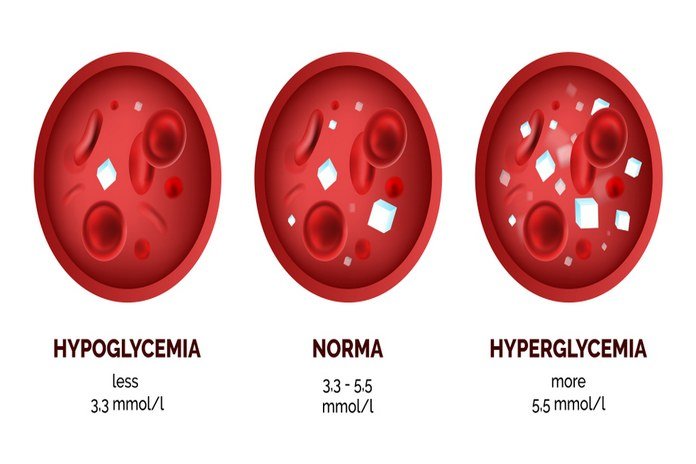
Hypoglycemia (hypo = low, glycemia = glucose/sugar), is one of the metabolic disorders in which the level of blood glucose usually falls at a lower level as compared to the average level of blood glucose. The majority of the body’s energy source is present in the form of glucose. Usually, the condition of hypoglycemia arises due to the side effect of diabetes treatment. However, some other drugs and a variety of metabolic disorders can also become the cause of low blood glucose levels in many people. The people who do not suffer from the pre-diabetes, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome can also become the victim of hypoglycemia due to some rare medical disorders which result in lowering the blood sugar levels than the normal.Although hypoglycemia is not as such injurious to health, it requires immediate medical attention as the low blood glucose levels can cause fainting or unconsciousness in the patients of hypoglycemia. For the majority of the people, the glucose levels in the fasting state are near to 3.9 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) or 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), the levels of blood glucose below than this level serves as an alarming condition for hypoglycemia. The levels of blood glucose levels might be different among various individuals, and it is better to seek an accurate diagnosis from a specialist to be sure of the condition of hypoglycemia.
The treatment of hypoglycemia consists of steadily getting the level of blood glucose back to the normal range either with medications or by taking high-sugar drinks or foods. The intake of medications or glucose-rich foods or drinks is one of the short-term treatments and do not help in eradicating the condition of hypoglycemia. At the same time, the long-term treatment plan of hypoglycemia involves the identification and treatment of the root cause behind hypoglycemia. If the patients of hypoglycemia do not seek the proper treatment, they might suffer from complications like seizures, death or loss of consciousness.

