DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS DIAGNOSIS
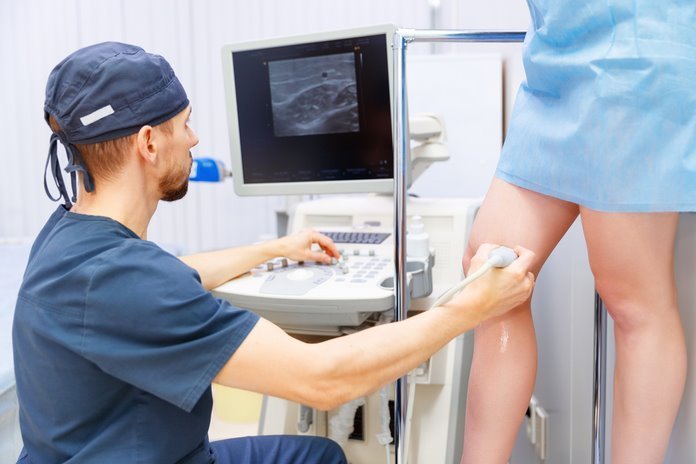
In the diagnosis of DVT, before going for any lab test, the medical history, family history, and physical examination of the patient are the major steps for determining the probability of DVT. As both these measures helps to determine the severity of the disease. Patients with clear history of immobilization, surgical procedure and leg trauma need further evaluation only to find out the severity and the degree of hypercoagulability. Diagnosis is typically done by duplex ultrasonography, which is the ultrasonography carried out with Doppler flow studies. There is a need for additional tests such as D-dimer testing if ultrasonography reports show positive results. These tests also depend upon the probability and severity of the conditions.
The methods carried out for diagnosis are:
Ultrasonography:
Ultrasonography is a technique, which is used to identify thrombi or blood clots by directly visualizing the venous lining, and by demonstrating abnormal vein compressibility. It can also be done with the help of Doppler flow studies that identify an impaired venous flow. The test is more efficient and productive in case of performing the diagnosis for femoral and popliteal vein thrombosis.

