Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter
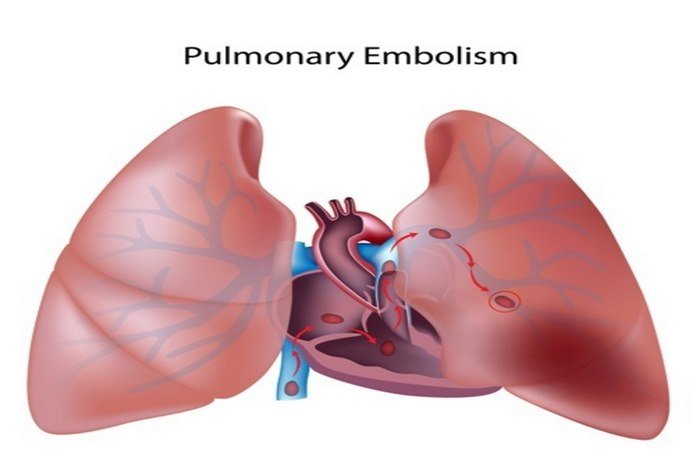
IVC filter is used for preventing Pulmonary embolism in patients with lower extremity DVT. As the name indicates it is placed in the Inferior Vena Cava just below the Renal veins via catheterization of an internal jugular or IVF femoral vein. It is mainly used in those patients, who are not able to use the Anticoagulant therapy for treating DVT or those patients who do not respond to adequate Anticoagulants. IVC filters are removable and can be used temporarily until another effective intervention.
Advantages of IVC filters:
- Reduce the risk of acute embolic complications.
- IVC filters can easily be removed.
Disadvantages:
- May induce a long-term serious complication due to the venous collateral’s development, providing a pathway for emboli to circumvent the filter, and also increase the risk of recurrent DVT.
- IVC filters can be dislodged or obstructed by a clot. Thus, patients with recurrent DVT or nonmodifiable risk factors for DVT may require anticoagulation despite the presence of an IVC filter.
- A clotted filter may cause bilateral lower extremity venous congestion including acute Phlegmasia cerulea dolens, lower body Ischemia, and Acute kidney injury. A dislodged filter must be removed, via angiographic technique or, if necessary, surgical methods.
- Its efficacy in preventing Pulmonary embolism is understudies.

