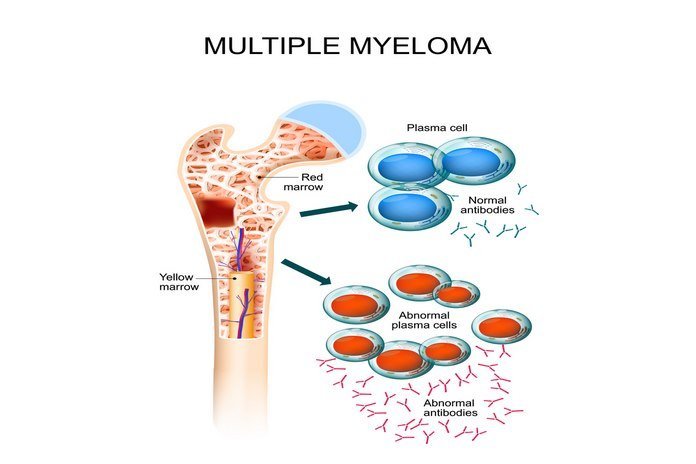
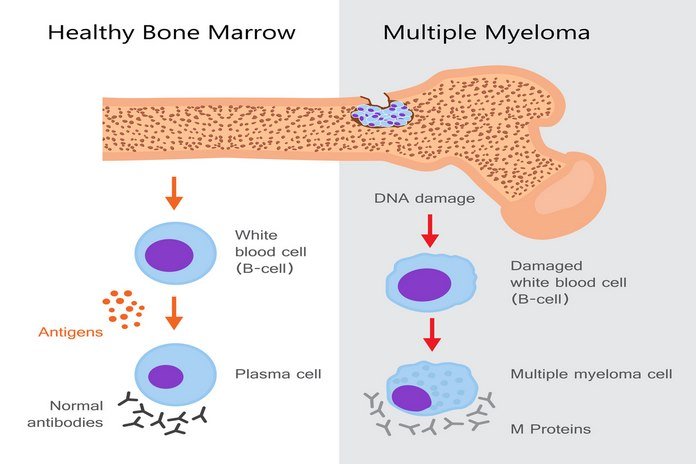
Multiple myeloma is also known as Kahler’s disease and plasma cell neoplasm. It is a type of plasma cell cancer. Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight against infections in the body.
In multiple myeloma, the plasma cells undergo abnormal division and become cancerous. During the cancerous condition, the plasma cells start producing a different kind of protein that accumulates in the blood and bones. This abnormal protein is called M protein or also known as paraprotein, M-spike, monoclonal protein, or monoclonal immunoglobulin. These cells trigger the production of some substances that weakens the bones, and these weaken areas are known as lytic lesions. This buildup of protein causes different symptoms like infections, anemia, weight loss, frequent urination, fatigue, fractures, fever, and some other health problems.
Multiple myeloma is diagnosed by different diagnostic procedures like bone marrow biopsy, imaging tests, and lab tests. Health care professionals use several therapies to treat multiple myeloma like targeted therapy, radiation, stem cell transplantation, and chemotherapy. In this article, you will learn about the symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis, and treatment of Multiple myeloma.
Types Of Multiple Myeloma
Smouldering multiple myeloma
This type does not cause any signs and symptoms, thats why this is called asymptomatic multiple myeloma. Most of the patients with smouldering multiple myeloma also develop active multiple myeloma.
Active multiple myeloma
This type is also known as symptomatic multiple myeloma because it shows the signs and symptoms of the disease. Following are the features of active multiple myeloma:
- Osteolytic lesions
- Weakened bones
- Hypercalcemia
- Anemia
- Kidney failure
- Plasmacytoma
- M-protein in the blood and urine
- Classification on the basis antibodies:
Multiple myeloma is also classified based on antibodies produced by cancerous cells. Five of these types are the following:
- IgD
- IgE
- IgM
- IgG
- IgA
Classification based on the number of chromosomes in the myeloma cells
Hyperdiploid multiple myeloma (HMM): In this type, the myeloma cells have higher than the usual number of chromosomes. HMM is generally not very aggressive and counts for almost 45 percent of cases of multiple myeloma.
Non-hyperdiploid or hypodiploid Multiple Myeloma: In this condition, the myeloma cells have fewer chromosomes than usual.