Surgery
The obesity surgical treatment is also well-known as weight loss surgery or bariatric surgery. Surgery is recently the most beneficial treatment for obesity resulting in sustainable weight loss and durable weight loss and accompanying improvements of health. Before you might know about operations that utilize to cure obesity, you want to know a bit about the method of digestion. The process of breaking your food down into the substances utilized by the body is also known as digestion. Digestion starts in the mouth where the chewing of food into small substances. After consumption, the food passes through the stomach, esophagus, and intestines (bowels) also known as the digestive tract. (9)
As the food passes by the digestive tract, it might be broken down by the digestive juices and enzymes. Once the breakdown occurs, individual food components such as carbohydrates, proteins, and other nutrients absorb into your small intestine wall. Different food substances absorb in various parts of the small intestine like the jejunum, duodenum, and ileum. The process is done by the strong acids present in the bile and stomach and in the duodenum pancreatic enzymes occur. Food particles that do not digest accumulate in the large intestine (colon). They remove from your body in the form of feces.
Bariatric Surgery Criteria
Candidates of weight loss surgery must complete the following criteria:
- Attempt non-surgical weight loss treatment previously and do not achieve the results of long-term weight loss
- Body mass index (BMI) is higher than 40 or a BMI must be 35 having obesity-related medical conditions such as sleep apnea, heart diseases, diabetes, high blood lipids, and hypertension
- Acceptable medical conditions for surgery
- Motivates and well-informed for long-term follow-up to gain substantial loss of weight
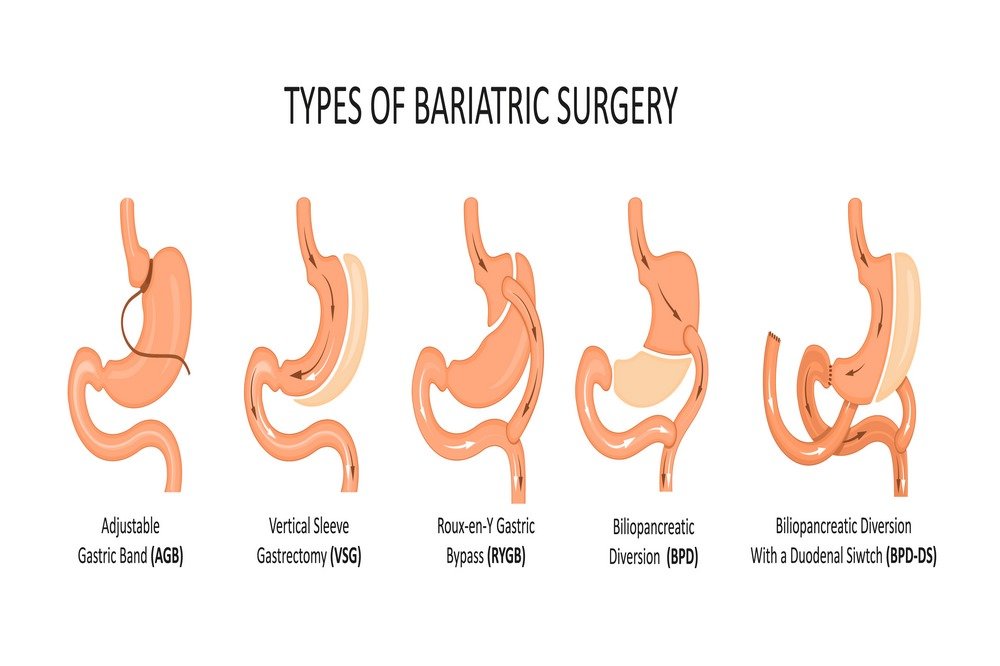
Bariatric surgery (weight loss surgery) classifications:
Surgeries that are present for weight loss are classified in the following:
- Malabsorptive methods that interfere with the absorption of food from the digestive tract
- Restrictive methods that reduce the food intake amount by lowering your stomach size
- Malabsorptive procedures and combined restrictive
The two most occurring operations for weight loss in the United States are an adjustable gastric band (AGB) and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Both methods can be performed laparoscopically with small incisions in comparison to those traditional open methods (laparotomy). Small incisions result in early ambulation, less pain, and rapid postoperative recovery and reduce the chance of complications of wound (fluid collection, wound infection, and hernia). Careful preoperative patient selection, screening, education, and preparation are essential for postoperative success.
A brief multidisciplinary scheme to patient’s education and screening, consisting of consultation with a psychologist, dietitian, bariatric surgeon, and internist is mandatory. In the cases of selection, pulmonary, cardiac, and endocrine evaluation might be required. Patients must have realistic expectations and an obvious understanding of risks, benefits, and long-term tasks of surgical treatment. While there are various operative procedures of bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass, vertical banded gastroplasty, laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion. These procedures are performed for weight loss and limit food absorption. Also, a small stomach pouch connects to the small intestine for small food intake.
