Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Treatment
If your child has been diagnosed with hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), then you may be wondering “how do you treat HUS?” The short answer is that there isn’t a specific treatment. Your doctor will work towards relieving some of your child’s symptoms while they wait for their body to recover naturally.(7)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome is a disease of the vascular system resulting from the presence of certain bacteria in the intestinal tract. Uncomplicated cases can be treated with fluids and antibiotics, but the condition can be fatal. Complicated cases, however, may be treated with specific treatment options such as plasma exchange.
Fluid Replacement
Fluid replacement is the key to treating HUS. Fluids include;
Electrolytes replacement
Replacing missing electrolytes is an extremely significant part of treating hemolytic uremic syndrome. With this treatment, the body is replenished with electrolytes. Electrolytes include minerals such as magnesium, calcium, and potassium. Fluid replacement increases blood flow to the kidneys as well. In addition to administring intravenous fluids, your doctor may advise you to increase your fluid intake by drinking more water-based drinks or electrolyte solutions.
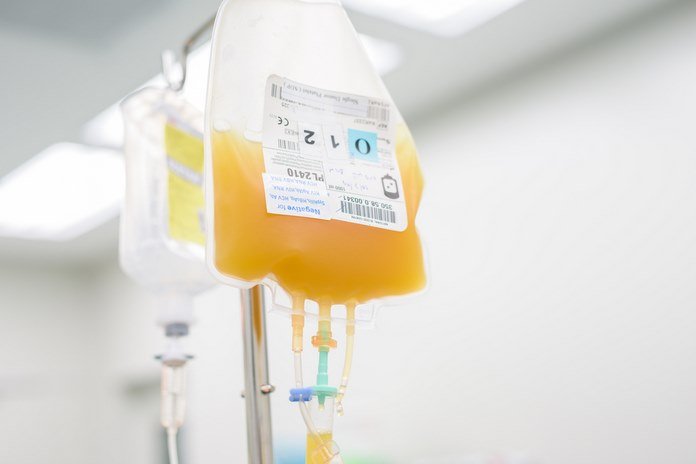
RBCs transfusion
HUS causes kidneys to stop working properly. It triggers breakdown of the red blood cells (RBCs) and clogging of tiny blood vessels throughout the body – leading to anemia. Many patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) need a blood transfusion. A donated blood product may also be given to stem the bleeding. Red blood cell transfusion can help treat and reverse symptoms of anemia – including fatigue, chills, shortness of breath, dark urine, rapid heart rate, and yellow skin.
Platelets transfusion
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a serious disorder of blood coagulation that is most often caused by a bacterial infection that has spread through the bloodstream, usually caused by E. coli. Hemolysis, which may mean destruction of red blood cells, occurs in HUS most often due to the red cell membrane being disrupted by activation of platelets. Through the destruction of red blood cells and platelets, hemolysis results in the generation of substances causing injury to many organs and organ systems.
Transfusion platelets help your blood clot more easily and quickly and can help reduce the complications due to excessive bleeding.

