Vitamin B12 Deficiency Causes
The deficiency of vitamin B12 has three primary underlying causes:
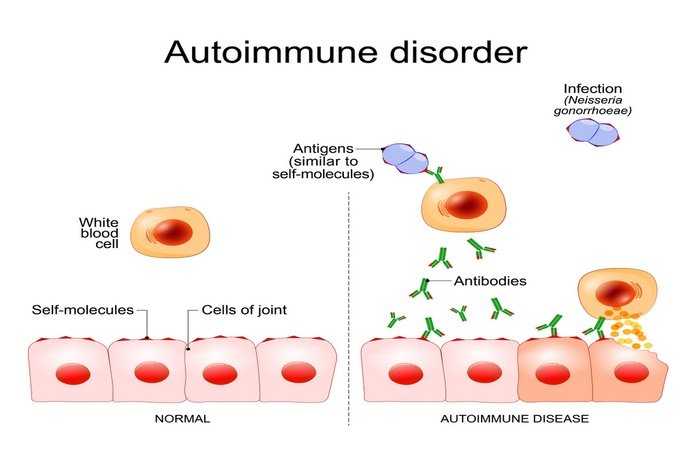
- Autoimmune disorders: Pernicious anemia is a type of autoimmune disorder in which the antibodies against intrinsic factor start producing. Anti-intrinsic factor antibodies tend to bind and inhibit the normal activity of the intrinsic factor. Hence, which results in an inability of vitamin B12 to attain absorption by the ileum.
- Dietary insufficiencies: Our body stores vitamin B12 in excess amounts in the liver, but patients who are following a strict vegan diet for almost a period of three years might develop vitamin B12 deficiency due to the lack of proper dietary intake.
- Malabsorption: Parietal cells lining the stomach walls produce intrinsic factor, so any patient with a history of gastric surgery might be at a risk of developing vitamin B12 deficiency. As the new alimentary pathway bypasses the location of intrinsic factor production, there can be problems arising in the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine. Any damage to the small intestine such as inflammation that occurs due to celiac disease or tapeworm infection might also lead to vitamin B12 deficiency. In people with normal production of intrinsic factor, damage to the terminal portion of the ileum like in surgical resection due to Crohn’s disease can lead to malabsorption of vitamin B12.
People who are at risk of developing vitamin B12 deficiency include:
- People on diabetic drugs like metformin
- People who are purely vegetarian
- The elderly
- People taking antacid drugs for longer time
- People having bowel parts removal surgery
