Types Of Pulmonary Embolism
Types on the basis of location of blood clots
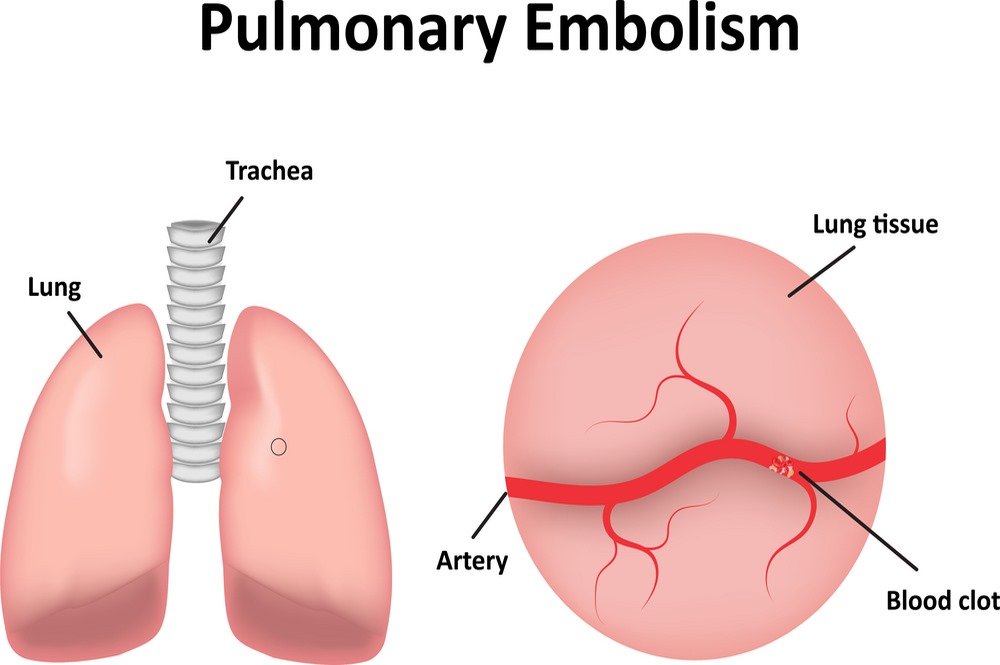
Pulmonary embolism can be of various types depending on the situation of the patient, the severity of the symptoms, and the location of blood clot formation. The location of blood clots changes progressively from smaller branches of the pulmonary artery to the formation of larger blood clots in the main pulmonary artery in lungs which disrupts the normal functioning of the lungs. Considering the location of the blood clot into pulmonary artery, following are some types of pulmonary embolism:
- Saddle pulmonary embolism (PE)
Saddle pulmonary embolism refers to the larger clot into the major pulmonary artery and is the major pulmonary embolism that gets on the bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk moving from the left to right of the pulmonary arteries. If a patient gets the diagnosis of saddle pulmonary embolism, it means it is life-threatening and requires immediate medical assistance.
- Lobar pulmonary embolism (PE)
Lobar pulmonary embolism (PE) refers to the occurrence of blood clots into big branches and segments of the pulmonary artery. Lobar pulmonary embolism involves multiple blood clots wedging at different segments of the pulmonary arteries.
- Distal pulmonary embolism (PE)
Distal pulmonary embolism (PE) refers to the presence of blood clots dispersing into small branches of the pulmonary artery. Small thrombi wedge in the distal arteries of the lungs travelling from the lower extremities and result in less hemodynamic compromise but cause more pleuritic chest pain. There is occasional infarction of the lungs in distal pulmonary embolism which causes ineffective gas exchange at the alveolar-arteriolar level leading to lower oxygen levels in the blood.
