Types on The Basis Of The Severity Of Symptoms
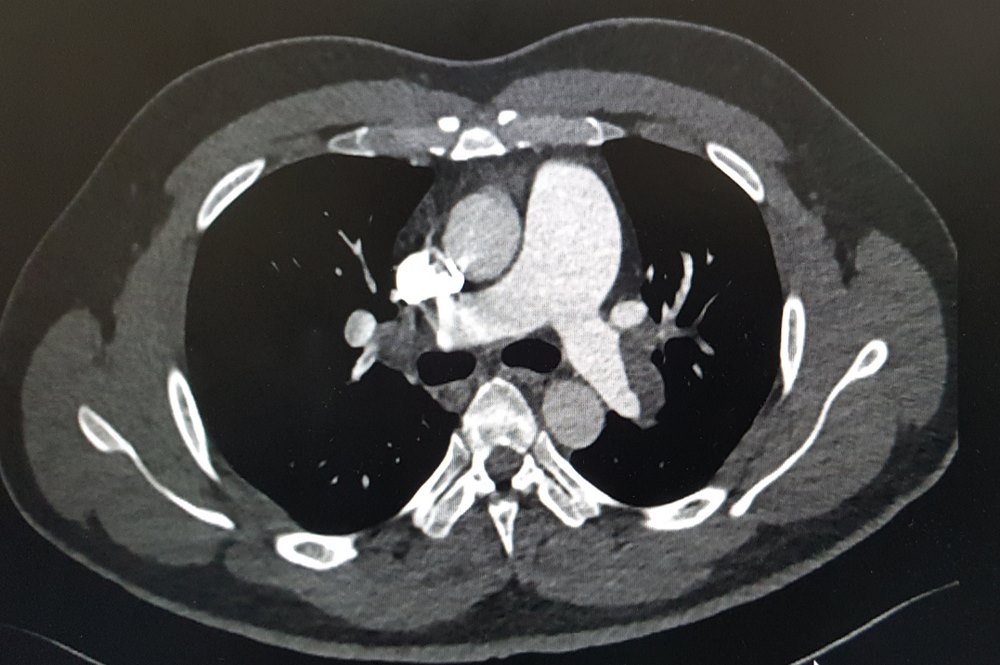
The doctors also characterize pulmonary embolism into different types depending on the severity of the embolisms and how symptomatic a patients is. The doctors consider how sick a person is by looking at the risk of serious complications or premature death. The severity of a patient’s condition also depends upon on the blood pressure, functionality of the lungs, and regularity of heart beats in a certain patient. Moreover, to determine what type of pulmonary embolism a person is going through, the healthcare professionals perform a series of imaging, scanning, and blood tests. The treatment choices are also different for each types of pulmonary embolism. Following is the characterization of pulmonary embolism on the basis of severity of the symptoms in a person: [6]
- Massive or acute pulmonary embolism
Massive pulmonary embolism is the high risk type of pulmonary embolism which includes sustainable hypotension with a systolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or less.
- Sub-massive pulmonary embolism
Sub-massive pulmonary embolism is known as the intermediate risk type of pulmonary embolism in which there is normal blood pressure with reports of right ventricular dysfunction. Also, there is elevation of myocardial necrosis in patients with sub-massive pulmonary embolism which indicates the damage happening to the heart due to the blood clots.
- Non-massive pulmonary embolism
Non-massive pulmonary embolism is also known as low-risk type of pulmonary embolism in which there is slight drop in blood pressure levels. There are no severe symptoms in this type of pulmonary embolism.
