Pleural Effusion
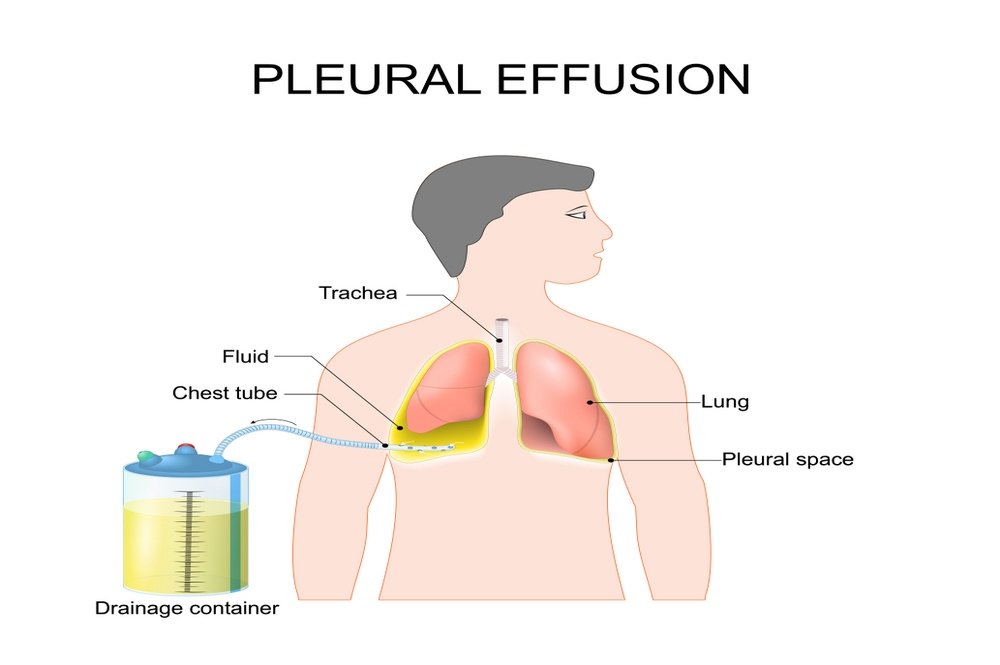
Pleural effusion refers to “water on the lungs” and is a condition in which fluid starts building up among the layers of thin membranes that surround your lungs i.e., the pleura. Pulmonary embolism is the fourth major cause of pleural effusion after the side effects of open-heart surgery, cirrhosis, and heart failure. Symptoms of pleural effusion include chest pain, a dry cough, and shortness of breath. Treatment of pulmonary embolism can directly help in resolving the condition of pleural effusion. However, in severe cases of pleural effusion, doctors perform a procedure to drain excess fluid from the lungs to assist normal breathing.

