Sickle cell anemia is known as a group of disorders called sickle cell disease. The essential thing to consider is that sickle cell anemia is an inherited red blood cell disorder. There are not healthy red blood cells for caring for oxygen throughout the body.
The flexible and round red blood cells can move easily from the blood vessels, but in sickle cell anemia, the red blood shaped like sickles and crescent moons. The cells also get the shape of sticky cells and rigid cells that easily get stuck in small blood vessels. These cells slow or block the blood flow with oxygen to all parts of the body. There is a great need to know, no cure for people with sickle cell anemia. However, some treatments can relieve pain or also help prevent complications associated with the disease.
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease. It affects the production of hemoglobin that is the component of the red blood cells. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from the oxygen-rich environment to the body tissues’ oxygen-poor environment. However, in sickle cell anemia patients, the hemoglobin is abnormal. The body part’s with low oxygen level allows the abnormal hemoglobin sticks together for forming clumps. These clumps cause the normally disc-shaped red blood cells to become shaped like crescents and sickles.
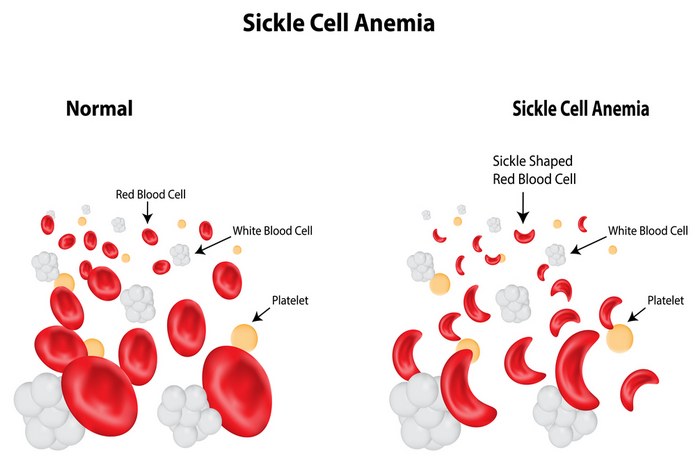
Furthermore, the abnormal cells obstruct the small blood vessels, and this obstruction also causes recurring painful episodes or sickle cell pain crises. Interrupted blood flow also causes tissue damage.
The abnormal hemoglobin causes sickle cell anemia is known as hemoglobin S. the sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease that is usually carried as an autosomal recessive trait. It means that both parents must carry the hemoglobin S gene. Each child would get that gene and have one chance in four of having sickle cell anemia

